Luteolin: A Flavonoid that Has Multiple Cardio-Protective Effects and Its Molecular Mechanisms
- PMID: 29056912
- PMCID: PMC5635727
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00692
Luteolin: A Flavonoid that Has Multiple Cardio-Protective Effects and Its Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
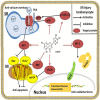
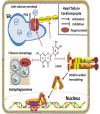
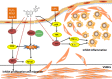
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) has become the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. A well-monitored diet with a sufficient intake of fruits and vegetables has been confirmed as a primary prevention of CVD. Plant constituents such as flavonoids have been shown to confer healthy benefits. Luteolin (Lut), a kind of flavonoid, possesses anti-oxidative, anti-tumor, and anti-inflammatory properties. Recent scientific literature has reported the cardiac protective effects of Lut in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, the aim of this review is to provide an update and detailed overview with cardio-protective molecular mechanisms of Lut with a focus on multiple intrinsic and extrinsic effectors. We further explore how these mechanisms participate in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, heart failure (HF) and atherosclerosis (AS). A proper understanding of the cardiovascular protective effects and the relative mechanisms of Lut may provide the possibility of new drug design and development for CVD. With the previous studies mainly focused on basic research, we need to advance the prospects of its further clinical utilization against CVD, large prospective clinical trials of Lut are needed to observe its therapeutic effects on patients with I/R injury, HF and AS, especially on the effective therapeutic dosage, and safety of long-term administration.
Keywords: I/R injury; atherosclerosis; cardio-protection; heart failure; luteolin; target effectors.
Figures

References
-
- Bogoyevitch M. A., Gillespiebrown J., Ketterman A. J., Fuller S. J., Benlevy R., Ashworth A., et al. (1996). Stimulation of the stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase subfamilies in perfused heart. p38/RK mitogen-activated protein kinases and c-Jun N-terminal kinases are activated by ischemia/reperfusion. Circ. Res. 79 162–173. 10.1161/01.RES.79.2.162 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

