Pineal Gland Tumor but not Pinealoma: A Case Report
- PMID: 29057188
- PMCID: PMC5647127
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1576
Pineal Gland Tumor but not Pinealoma: A Case Report
Abstract
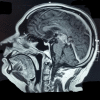
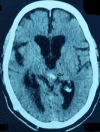
The pineal gland is a small pinecone-shaped and functionally endocrine structure located in the epithalamus region. Developmentally, the pineal gland is considered as a part of the epithalamus. It plays a role in the entrainment of the circadian rhythms of an organism by producing melatonin, a functionally important hormone. Lesions of the pineal region are rare compared to other parts of the brain. A lesion may be tumorous or non-tumorous in nature. The most common lesions are tumors that are pineal parenchymal tumors (PPT) in origin. Gliomas are the second most common tumors in the pineal region. We report a case of a high-grade oligodendroglioma, not commonly seen in the pineal region, in a 45-year-old male. The patient was suspected to have a mass in the pineal region on a computed tomography (CT) scan and histology confirmed the diagnosis of oligodendroglioma. This is a unique case because only five such cases have been reported so far.
Keywords: headache; oligodendroglioma; pineal gland; tumor; visual disturbance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Histological analysis of lesions of the pineal region: a retrospective study of 12 years. Kumar P, Tatke M, Sharma A, et al. Pathol Res Pract. 2006;202:85–92. - PubMed
-
- Oligodendroglioma: diagnosis and prognosis. Bruner JM. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3313607. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1987;4:251–261. - PubMed
-
- Oligodendroglioma: an analysis of prognostic factors and treatment results. Allam A, Radwi A, El Weshi A, et al. http://journals.lww.com/amjclinicaloncology/Abstract/2000/04000/Oligoden.... Am J Clin Oncol. 2000;23:170–175. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources