Genome-wide association study of alcohol use disorder identification test (AUDIT) scores in 20 328 research participants of European ancestry
- PMID: 29058377
- PMCID: PMC6988186
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.12574
Genome-wide association study of alcohol use disorder identification test (AUDIT) scores in 20 328 research participants of European ancestry
Abstract
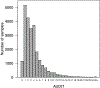
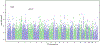
Genetic factors contribute to the risk for developing alcohol use disorder (AUD). In collaboration with the genetics company 23andMe, Inc., we performed a genome-wide association study of the alcohol use disorder identification test (AUDIT), an instrument designed to screen for alcohol misuse over the past year. Our final sample consisted of 20 328 research participants of European ancestry (55.3% females; mean age = 53.8, SD = 16.1) who reported ever using alcohol. Our results showed that the 'chip-heritability' of AUDIT score, when treated as a continuous phenotype, was 12%. No loci reached genome-wide significance. The gene ADH1C, which has been previously implicated in AUD, was among our most significant associations (4.4 × 10-7 ; rs141973904). We also detected a suggestive association on chromosome 1 (2.1 × 10-7 ; rs182344113) near the gene KCNJ9, which has been implicated in mouse models of high ethanol drinking. Using linkage disequilibrium score regression, we identified positive genetic correlations between AUDIT score, high alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking. We also observed an unexpected positive genetic correlation between AUDIT and educational attainment and additional unexpected negative correlations with body mass index/obesity and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. We conclude that conducting a genetic study using responses to an online questionnaire in a population not ascertained for AUD may represent a cost-effective strategy for elucidating aspects of the etiology of AUD.
Keywords: AUDIT; GWAS; alcohol use disorder; alcohol-metabolizing enzymes; complex traits; genetic.
© 2017 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures
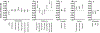
References
-
- Agrawal A, Freedman ND, Cheng Y-C, Lin P, Shaffer JR, Sun Q, Taylor K, Yaspan B, Cole JW, Cornelis MC, DeSensi RS, Fitzpatrick A, Heiss G, Kang JH, O’Connell J, Bennett S, Bookman E, Bucholz KK, Caporaso N, Crout R, Dick DM, Edenberg HJ, Goate A, Hesselbrock V, Kittner S, Kramer J, Nurnberger JI, Qi L, Rice JP, Schuckit M, van Dam RM, Boerwinkle E, Hu F, Levy S, Marazita M, Mitchell BD, Pasquale LR, Bierut LJ & GENEVA Consortium (2012) Measuring alcohol consumption for genomic meta-analyses of alcohol intake: opportunities and challenges. Am J Clin Nutr 95:539–547. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aguado C, Colón J, Ciruela F, Schlaudraff F, Cabañero MJ, Perry C, Watanabe M, Liss B, Wickman K & Luján R (2008) Cell type-specific subunit composition of G protein-gated potassium channels in the cerebellum. J Neurochem 105:497–511. - PubMed
-
- Allen J, Litten R, Fertig J & Babor T (1997) A Review of Research on the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT). Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21:613–619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

