Synthetic hydrogels for human intestinal organoid generation and colonic wound repair
- PMID: 29058719
- PMCID: PMC5664213
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3632
Synthetic hydrogels for human intestinal organoid generation and colonic wound repair
Abstract
In vitro differentiation of human intestinal organoids (HIOs) from pluripotent stem cells is an unparalleled system for creating complex, multicellular three-dimensional structures capable of giving rise to tissue analogous to native human tissue. Current methods for generating HIOs rely on growth in an undefined tumour-derived extracellular matrix (ECM), which severely limits the use of organoid technologies for regenerative and translational medicine. Here, we developed a fully defined, synthetic hydrogel based on a four-armed, maleimide-terminated poly(ethylene glycol) macromer that supports robust and highly reproducible in vitro growth and expansion of HIOs, such that three-dimensional structures are never embedded in tumour-derived ECM. We also demonstrate that the hydrogel serves as an injection vehicle that can be delivered into injured intestinal mucosa resulting in HIO engraftment and improved colonic wound repair. Together, these studies show proof-of-concept that HIOs may be used therapeutically to treat intestinal injury.
Figures
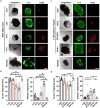
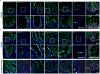
 ) or Matrigel™ (■) (n = 6 organoids for PEG-4MAL and n = 4 organoids for Matrigel™ per time-point). Repeated measures two-way ANOVA showed no significant difference between matrix types (P > 0.05). Line represents the mean of the individual data points at each time-point. (d,e) Fluorescence microscopy images of a HIO at 21 d after encapsulation in 4.0% PEG-4MAL-RGD hydrogel or Matrigel™ and labeled for (d) β-CATENIN, proliferative cells (KI67), and (e) epithelial apical polarity (EZRIN) and tight junctions (ZO-1). DAPI, counterstain. “L” indicates HIO lumen. Bars, 100 μm. Three independent experiments were performed and data is presented for one of the experiments. Every experiment was performed with 6 gel samples per experimental group (PEG-4MAL, Matrigel™). Source data are available in Supplementary Table 1.
) or Matrigel™ (■) (n = 6 organoids for PEG-4MAL and n = 4 organoids for Matrigel™ per time-point). Repeated measures two-way ANOVA showed no significant difference between matrix types (P > 0.05). Line represents the mean of the individual data points at each time-point. (d,e) Fluorescence microscopy images of a HIO at 21 d after encapsulation in 4.0% PEG-4MAL-RGD hydrogel or Matrigel™ and labeled for (d) β-CATENIN, proliferative cells (KI67), and (e) epithelial apical polarity (EZRIN) and tight junctions (ZO-1). DAPI, counterstain. “L” indicates HIO lumen. Bars, 100 μm. Three independent experiments were performed and data is presented for one of the experiments. Every experiment was performed with 6 gel samples per experimental group (PEG-4MAL, Matrigel™). Source data are available in Supplementary Table 1.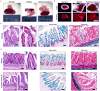
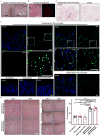
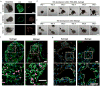
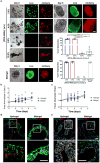
 ) or Matrigel™-grown HIOs in hydrogel (
) or Matrigel™-grown HIOs in hydrogel (
 ) and saline-injected HIOs (
) and saline-injected HIOs (
 ), only hydrogel (
), only hydrogel (
 ), or no injection group (X) (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). Bar, 500 μm. Two independent experiments were performed and data is presented for one of the experiments. Experiments performed with 4 mice per experimental group (five colonic wounds/injections per mouse; a-e). Source data are available in Supplementary Table 1.
), or no injection group (X) (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). Bar, 500 μm. Two independent experiments were performed and data is presented for one of the experiments. Experiments performed with 4 mice per experimental group (five colonic wounds/injections per mouse; a-e). Source data are available in Supplementary Table 1.References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR062368/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119215/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R29 DK055679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI116482/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK085532/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007505/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103141/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL115372/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055679/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR062920/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DE007057/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007315/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK089763/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085532/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089763/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK059888/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

