A structural explanation for the low effectiveness of the seasonal influenza H3N2 vaccine
- PMID: 29059230
- PMCID: PMC5667890
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006682
A structural explanation for the low effectiveness of the seasonal influenza H3N2 vaccine
Abstract
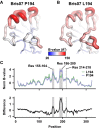
The effectiveness of the annual influenza vaccine has declined in recent years, especially for the H3N2 component, and is a concern for global public health. A major cause for this lack in effectiveness has been attributed to the egg-based vaccine production process. Substitutions on the hemagglutinin glycoprotein (HA) often arise during virus passaging that change its antigenicity and hence vaccine effectiveness. Here, we characterize the effect of a prevalent substitution, L194P, in egg-passaged H3N2 viruses. X-ray structural analysis reveals that this substitution surprisingly increases the mobility of the 190-helix and neighboring regions in antigenic site B, which forms one side of the receptor binding site (RBS) and is immunodominant in recent human H3N2 viruses. Importantly, the L194P substitution decreases binding and neutralization by an RBS-targeted broadly neutralizing antibody by three orders of magnitude and significantly changes the HA antigenicity as measured by binding of human serum antibodies. The receptor binding mode and specificity are also altered to adapt to avian receptors during egg passaging. Overall, these findings help explain the low effectiveness of the seasonal vaccine against H3N2 viruses, and suggest that alternative approaches should be accelerated for producing influenza vaccines as well as isolating clinical isolates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Comment in
-
Influenza H3N2 Vaccines: Recent Challenges.Trends Microbiol. 2018 Feb;26(2):87-89. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.12.003. Trends Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29268980
References
-
- Wiley DC, Wilson IA, Skehel JJ. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981;289(5796):373–8. . - PubMed
-
- Wiley DC, Skehel JJ. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wu NC, Young AP, Al-Mawsawi LQ, Olson CA, Feng J, Qi H, et al. High-throughput profiling of influenza A virus hemagglutinin gene at single-nucleotide resolution. Sci Rep. 2014;4:4942 doi: 10.1038/srep04942 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4018626. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thyagarajan B, Bloom JD. The inherent mutational tolerance and antigenic evolvability of influenza hemagglutinin. eLife. 2014;3:e03300 doi: 10.7554/eLife.03300 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4109307. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

