Association analysis identifies 65 new breast cancer risk loci
- PMID: 29059683
- PMCID: PMC5798588
- DOI: 10.1038/nature24284
Association analysis identifies 65 new breast cancer risk loci
Abstract
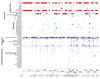
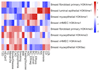
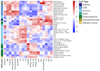
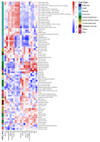
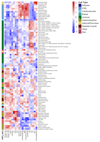
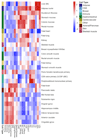
Breast cancer risk is influenced by rare coding variants in susceptibility genes, such as BRCA1, and many common, mostly non-coding variants. However, much of the genetic contribution to breast cancer risk remains unknown. Here we report the results of a genome-wide association study of breast cancer in 122,977 cases and 105,974 controls of European ancestry and 14,068 cases and 13,104 controls of East Asian ancestry. We identified 65 new loci that are associated with overall breast cancer risk at P < 5 × 10-8. The majority of credible risk single-nucleotide polymorphisms in these loci fall in distal regulatory elements, and by integrating in silico data to predict target genes in breast cells at each locus, we demonstrate a strong overlap between candidate target genes and somatic driver genes in breast tumours. We also find that heritability of breast cancer due to all single-nucleotide polymorphisms in regulatory features was 2-5-fold enriched relative to the genome-wide average, with strong enrichment for particular transcription factor binding sites. These results provide further insight into genetic susceptibility to breast cancer and will improve the use of genetic risk scores for individualized screening and prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_PC_14105/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 CA194393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 20861/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA184585/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA092044/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100374/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098758/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA199277/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164917/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA092049/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG006623/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA176785/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA089085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 15106/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P50 CA125183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097396/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA176726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103504/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA064277/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 20411/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- D43 TW009112/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA122171/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA148667/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA077398/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA132839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG009979/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA159868/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121941/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101244/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- A16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA182910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA192393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- P30 CA006927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA120120/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 CA169004/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 19187/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

