Elevated microRNA-129-5p level ameliorates neuroinflammation and blood-spinal cord barrier damage after ischemia-reperfusion by inhibiting HMGB1 and the TLR3-cytokine pathway
- PMID: 29061187
- PMCID: PMC5654055
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-017-0977-4
Elevated microRNA-129-5p level ameliorates neuroinflammation and blood-spinal cord barrier damage after ischemia-reperfusion by inhibiting HMGB1 and the TLR3-cytokine pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Elevated microRNA-129-5p level ameliorates neuroinflammation and blood-spinal cord barrier damage after ischemia-reperfusion by inhibiting HMGB1 and the TLR3-cytokine pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Dec 28;18(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02345-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34963474 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
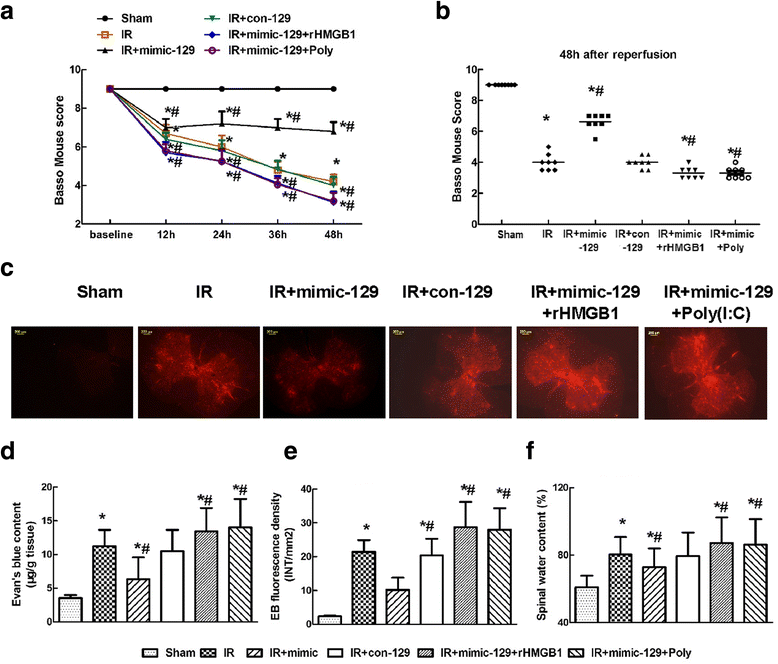
Background: Ischemia-reperfusion (IR) affects microRNA (miR) expression and causes substantial inflammation. Multiple roles of the tumor suppressor miR-129-5p in cerebral IR have recently been reported, but its functions in the spinal cord are unclear. Here, we investigated the role of miR-129-5p after spinal cord IR, particularly in regulating high-mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) and the Toll-like receptor (TLR)-3 pathway.
Methods: Ischemia was induced via 5-min occlusion of the aortic arch. The relationship between miR-129-5p and HMGB1 was elucidated via RT-PCR, western blotting, and luciferase assays. The cellular distribution of HMGB1 was determined via double immunofluorescence. The effect of miR-129-5p on the expression of HMGB1, TLR3, and downstream cytokines was evaluated using synthetic miRs, rHMGB1, and the TLR3 agonist Poly(I:C). Blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB) permeability was examined by measuring Evans blue (EB) dye extravasation and the water content.
Results: The temporal miR-129-5p and HMGB1 expression profiles and luciferase assay results indicated that miR-129-5p targeted HMGB1. Compared with the Sham group, the IR group had higher HMGB1 immunoreactivity, which was primarily distributed in neurons and microglia. Intrathecal injection of the miR-129-5p mimic significantly decreased the HMGB1, TLR3, interleukin (IL)-1β and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α levels and the double-labeled cell count 48 h post-surgery, whereas rHMGB1 and Poly(I:C) reversed these effects. Injection of miR-129-5p mimic preserved motor function and prevented BSCB leakage based on increased Basso Mouse Scale scores and decreased EB extravasation and water content, whereas injection rHMGB1 and Poly(I:C) aggravated these injuries.
Conclusions: Increasing miR-129-5p levels protect against IR by ameliorating inflammation-induced neuronal and BCSB damage by inhibiting HMGB1 and TLR3-associated cytokines.
Keywords: Blood-spinal cord barrier; High-mobility group box-1; Ischemia-reperfusion injury; MicroRNAs; Toll-like receptor 3.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of China Medical University and performed in compliance with institutional guidelines under approved protocols.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures






References
-
- Li XQ, Lv HW, Tan WF, Wang ZL, Fang B, Ma H. MiR-27a ameliorates inflammatory damage to the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by down-regulating TICAM-2 of the TLR4 signaling pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:25. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0246-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

