Intranuclear Inclusions in Renal Tubular Epithelium in Immunodeficient Mice Stain with Antibodies for Bovine Papillomavirus Type 1 L1 Protein
- PMID: 29061933
- PMCID: PMC5644623
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci2020084
Intranuclear Inclusions in Renal Tubular Epithelium in Immunodeficient Mice Stain with Antibodies for Bovine Papillomavirus Type 1 L1 Protein
Abstract
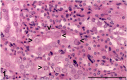
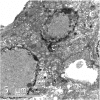
The kidneys from six immunodeficient mice examined by Cerberus Sciences and the Animal Resources Centre, displayed karyomegaly with pale eosinophilic, intranuclear inclusions upon histopathological examination. Electron microscopy performed on kidney tissue from 5/6 mice demonstrated margination of the chromatin in large nuclei. Laboratory tests were used to detect nucleic acid of papillomaviruses, polyomaviruses, circoviruses and anelloviruses (4/6 mice), a specific PCR was used to detect murine polyomavirus (1/6), and a panel of serological tests was used to detect seroconversion to major murine pathogens (1/6). All molecular and serological tests were negative. Immunohistochemistry using polyclonal anti-bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV-1) L1 antibody, Camvir monoclonal anti-papillomavirus antibody (directed against the seven amino acids GFGAMDF found in human papillomavirus (HPV) 16 L1 protein), a commercially available mixture of two monoclonal antibodies, anti-BPV-1 L1/1H8 + Camvir antibodies, and a monoclonal anti-Hsc70 antibody revealed specific, positive staining of murine renal tubular epithelial intranuclear inclusions in 6/6 mice using the anti-BPV-1 L1 containing antibodies only. Methyl pyronin green, PAS and Feulgen histochemical reactions revealed that the intranuclear inclusions did not consist of RNA, DNA or carbohydrate. An immunohistochemical method now exists that can be used to confirm and evaluate suspected cases of murine inclusion body nephropathy.
Keywords: bovine papillomavirus type 1 L1 protein; intranuclear inclusions; mouse; renal tubular epithelium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baze W.B., Steinbach T.J., Fleetwood M.L., Blanchard T.W., Barnhart K.F., McArthur M.J. Karyomegaly and intranuclear inclusions in the renal tubules of sentinel ICR mice (Mus musculus) Comp. Med. 2006;56:435–438. - PubMed
-
- Rector A., Tachezy R., Van Doorslaer K., MacNamara T., Burk R.D., Sundberg J.P., Van Ranst M. Isolation and cloning of a papillomavirus from a North American porcupine by using multiply primed rolling-circle amplification: The Erethizon dorsatum papillomavirus type 1. Virology. 2005;331:449–456. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.10.033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bancroft J.D., Fredenburgh J.L., Grizzle W.E., Myers R.B. Proteins and nucleic acids. In: Bancroft J.D., Stevens M., editors. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. 5th ed. Churchill Livingstone; Edinburgh, UK: 2002. pp. 217–233.
-
- Australian Code for the Care and Use of Animals for Scientific Purposes. 8th ed. 2013. [(accessed on 5 June 2015)]. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/6YwpUvaz3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

