Obesity Increases Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase-3 Levels in the Hypothalamus of Mice
- PMID: 29062272
- PMCID: PMC5640777
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00313
Obesity Increases Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase-3 Levels in the Hypothalamus of Mice
Abstract
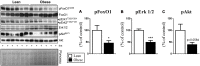
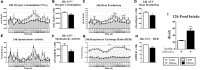
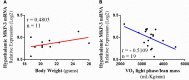
Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase 3 (MKP-3) has been involved in the negative regulation of insulin signaling. The absence of MKP-3 is also associated with reduced adiposity, increased energy expenditure and improved insulin sensitivity. The MKP-3 is known as the main Erk1/2 phosphatase and FoxO1 activator, which has repercussions on the gluconeogenesis pathway and hyperglycemia in obese mice. Recently, we showed that MKP-3 overexpression decreases FoxO1 phosphorylation in the hypothalamus of lean mice. However, the hypothalamic interaction between MKP-3 and FoxO1 during obesity was not investigated yet. Here, the MKP-3 expression and the effects on food intake and energy expenditure, were investigated in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. The results indicate that obesity in mice increased the MKP-3 protein content in the hypothalamus. This hypothalamic upregulation led to an increase of food intake, adiposity, and body weight. Furthermore, the obese mice with increased MKP-3 showed an insulin signaling impairment with reduction of insulin-induced FoxO1 and Erk1/2 phosphorylation in the hypothalamus. Moreover, a bioinformatics analysis of data demonstrated that hypothalamic MKP-3 mRNA levels were positively correlated with body weight and negatively correlated to oxygen consumption (VO2) in BXD mice. Taken together, our study reports that obesity is associated with increased protein levels of hypothalamic MKP-3, which is related to the reduction of FoxO1 and Erk1/2 phosphorylation in the hypothalamus as well as to an increase in body weight and a reduction in energy expenditure.
Keywords: MKP-3; food intake; hypothalamus; insulin; obesity.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

