Biobanking from the patient perspective
- PMID: 29062493
- PMCID: PMC5598087
- DOI: 10.1186/s40900-015-0001-z
Biobanking from the patient perspective
Abstract
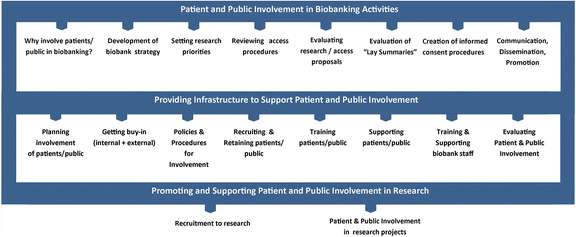
Plain english summary: Biobanks are collections of donations of biological material (DNA, cells, tissue etc.) and related data which are very valuable for research into human diseases. A variety of biobanks exist for example within hospitals, research institutes, pharmaceutical companies and patient organisations. The role of patients in biobanking is changing from being seen simply as donors, to actual collaborators in the design, development and the running of biobanks. In this article, we provide a number of examples of patients acting as partners at the heart of biobanking, where their voice and perspective is being seen and used as a valuable resource for the biobank. Our aim is that these examples can be used by those who work with patients in biobank-based research, to design future strategies for patient and public involvement in all biobanks.
Abstract: Biobanks and biobanking research plays an increasingly important role in healthcare research and delivery as health systems become more patient-centred and medicine becomes more personalised. There is also growing acceptance and appreciation of the value that patients, patient advocacy organisations and the public can bring as stakeholders in biobanking and more generally in research. Therefore, the importance of active, early and sustained engagement and involvement of patient and public representatives in biobanks will become increasingly relevant. Organising and facilitating patient and public involvement in biobanking takes considerable time and effort for all stakeholders involved. Therefore, for any biobank operator considering involving patients and the public in their biobanking activities, consideration of best practices, current guidance, ethical issues and evaluation of involvement will be important. In this article, we demonstrate that patients are much more than donors to biobanks-they are collaborators at the heart of biobanking with an important voice to identify perspective, which can be an extremely valuable resource for all biobanks to utilise. The case studies herein provide examples of good practice of patient involvement in biobanking as well as outcomes from these practices, and lessons learned. Our aim is to provide useful insights from these efforts and potential future strategies for the multiple stakeholders that work with patients and the public involved in biobank-based research.
Keywords: Biobank; Involvement; Partnering; Patient; Research.
Figures
References
-
- Commission E. Biobanks for Europe—a challenge for governance. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union; 2012.
-
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Affordable Healthcare Act 2010 (Internet). 2014. Available at: http://www.hhs.gov/healthcare/facts/timeline. Accessed 25 April 2014
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources