Patient and public involvement in primary care research - an example of ensuring its sustainability
- PMID: 29062502
- PMCID: PMC5611572
- DOI: 10.1186/s40900-016-0015-1
Patient and public involvement in primary care research - an example of ensuring its sustainability
Abstract
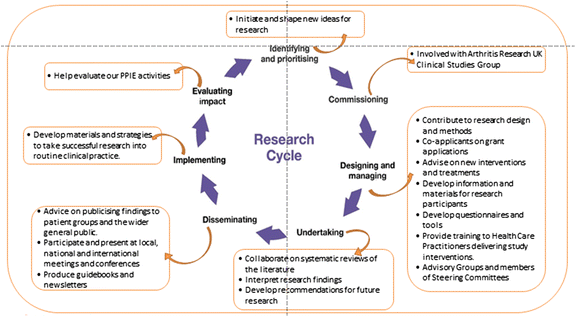
Background: The international literature on patient and public involvement (PPI) in research covers a wide range of issues, including active lay involvement throughout the research cycle; roles that patients/public can play; assessing impact of PPI and recommendations for good PPI practice. One area of investigation that is less developed is the sustainability and impact of PPI beyond involvement in time-limited research projects.
Methods: This paper focuses on the issues of sustainability, the importance of institutional leadership and the creation of a robust infrastructure in order to achieve long-term and wide-ranging PPI in research strategy and programmes.
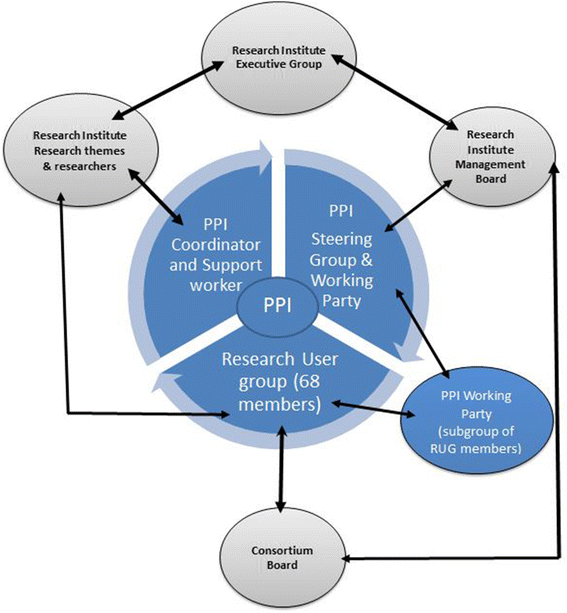
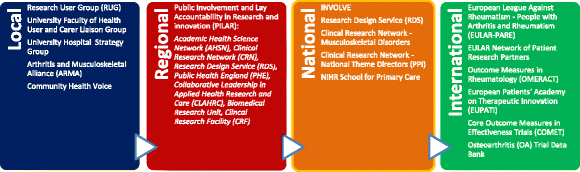
Results: We use the case of a Primary Care Research Centre to provide a historical account of the evolution of PPI in the Centre and identified a number of key conceptual issues regarding infrastructure, resource allocation, working methods, roles and relationships.
Conclusions: The paper concludes about the more general applicability of the Centre's model for the long-term sustainability of PPI in research.
Keywords: Impact; Patient and public involvement; Primary care research; Resource allocation; Sustainability of PPI.
Figures
References
-
- INVOLVE. Evidence Library; 2015. http://www.invo.org.uk/resource-centre/evidence-library/. Accessed 5 August 2015.
-
- de Wit M. Patient participation in rheumatology research. A four level responsive evaluation. Amsterdam: Vrije Universiteit; 2013.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

