A Complicated Case of Group B Streptococcus Empyema Necessitans
- PMID: 29062623
- PMCID: PMC5650258
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1591
A Complicated Case of Group B Streptococcus Empyema Necessitans
Abstract
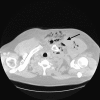
Empyema necessitans is a complication of a pleural space infection that dissects through the pleura into the soft tissues of the chest and skin. Due to the widespread availability of antibiotics, empyema necessitans is rare in modern medicine and is most commonly caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A 38-year-old immunocompetent male presented with left shoulder pain and his chest radiograph revealed a mass in the upper left lung and/or pleural space. He underwent multiple debridements of the chest wall due to a left chest wall abscess and empyema necessitans. All operative samples were positive for Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Streptococcus). The patient's clinical course was complicated by septic arthritis of the left sternoclavicular joint and first rib, vertebral osteomyelitis/discitis, and pelvic abscesses. This case report illustrates the pathogenic process of empyema necessitans and summarizes the clinical management for practicing clinicians. It also documents the second case of Streptococcus agalactiae-associated empyema necessitans, to our knowledge, with significantly greater disease extension than the first.
Keywords: empyema necessitans; group b streptococcus; pelvic abscess; septic arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Contemporary empyema necessitatis. Kono SA, Nauser TD. Am J Med. 2007;120:303–305. - PubMed
-
- A case of empyema necessitatis. Tonna I, Conlon CP, Davies RJ. Eur J Intern Med. 2007;18:441–442. - PubMed
-
- Management of empyema - Role of a surgeon. Gupta D, Sharma S. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2005;10:142–146.
-
- Empyema necessitatis in an infant: a rare surgical disease. Moore FO, Berne JD, McGovern TM, et al. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41:0–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources