Postoperative visual performance with a bifocal and trifocal diffractive intraocular lens during a 1-year follow-up
- PMID: 29062771
- PMCID: PMC5638973
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2017.10.08
Postoperative visual performance with a bifocal and trifocal diffractive intraocular lens during a 1-year follow-up
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate and compare the clinical outcomes with a diffractive bifocal and trifocal intraocular lens (IOL) during a 12-month follow-up.
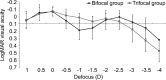
Methods: Prospective comparative study including 75 eyes of 38 patients (44-70y) undergoing uneventful cataract surgery. Each patient was randomly assigned to one type of IOL, bifocal (35 eyes) or trifocal (40 eyes). Visual, refractive, and contrast sensitivity changes were evaluated in a 12-month follow-up. The binocular defocus curve was also measured at 12mo postoperatively.
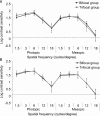
Results: No statistically significant differences between groups were found in postoperative uncorrected and corrected distance visual acuities (P≥0.276). Postoperative corrected near visual acuity (33 cm) was significantly better in the trifocal group during all follow-up (P≤0.004) as well as 6-month uncorrected near (P=0.008) and distance-corrected near visual acuities (P=0.016) (33/40 cm). Significantly better uncorrected intermediate and distance corrected-intermediate visual acuity were found during all follow-up in the trifocal group (P<0.001), which was consistent with differences among groups in binocular defocus curve. Differences among groups in contrast sensitivity were minimal, being only significant at 6 months for some low to medium spatial frequencies (P≤0.006).
Conclusion: Bifocal and trifocal diffractive IOLs are able to provide an effective visual restoration which is maintained during a 12-month follow-up, with a clear benefit of the trifocal IOL for the intermediate vision.
Keywords: bifocal intraocular lens; cataract surgery; contrast sensitivity; defocus curve; trifocal intraocular lens.
Figures
References
-
- Kohnen T, Titke C, Böhm M. Trifocal intraocular lens implantation to treat visual demands in various distances following lens removal. Am J Ophthalmol. 2016;161:71–77.e1. - PubMed
-
- Mojzis P, Majerova K, Hrckova L, Piñero DP. Implantation of a diffractive trifocal intraocular lens: one-year follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015;41(8):1623–1630. - PubMed
-
- Marques JP, Rosa AM, Quendera B, Silva F, Mira J, Lobo C, Castelo-Branco M, Murta JN. Quantitative evaluation of visual function 12 months after bilateral implantation of a diffractive trifocal IOL. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2015;25(6):516–524. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources