In situ cornea harvesting through the Red Cross Organization: a new approach to relieving severe cornea donor shortage in Chinese eye banks
- PMID: 29062783
- PMCID: PMC5638985
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2017.10.20
In situ cornea harvesting through the Red Cross Organization: a new approach to relieving severe cornea donor shortage in Chinese eye banks
Abstract
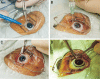
Corneal diseases are currently the second main cause of blindness in China. Although most of the corneal blindness could be treated by corneal transplantation, only about 10 000 operations were carried out each year owing to the severe shortage of corneal donors and limited eye bank programs. A feasible cornea donation program was established through the organization of the Red Cross, and in situ corneal removal techniques were developed to avoid conflicts with Chinese traditions of keeping the deceased intact. The number of donated corneas, which had a safe and secure quality, increased significantly year by year.
Keywords: cornea; donor; eye bank; transplantation.
Figures

References
-
- Xie HP, Li SY. Analysis of current status of eye bank construction in Western China. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2005;41(5):390–393. - PubMed
-
- Pan ZQ, Liu J, Wang L, Zhang M. Preliminary analysis on the status of the registered donators in Beijing Tongren Eye Banks. Chin J Ophthalmol. 2004;40(9):639–640.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
