Effect of Different Diets on Lifetime of Brown-Banded Cockroaches, Supella longipalpa (Blattodea: Blattellidae)
- PMID: 29062854
- PMCID: PMC5641618
Effect of Different Diets on Lifetime of Brown-Banded Cockroaches, Supella longipalpa (Blattodea: Blattellidae)
Abstract
Background: The brown-banded cockroach, Supella longipalpa, is not as common as the German cockroach in Iran. This species seeks out areas that are very warm most of the time, and prefer warmer area than what German cockroaches prefer. There is relationship between development of instars and diet of cockroaches. The aim of this study was to determine the effect of different diets on biology, life cycle on nymphal stages of S. longipalpa in laboratory condition prior to investigate the insecticide resistance status of this species in residence area in Iran.
Methods: The cockroaches were reared in the insectary of School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, condition and the population divided in four equal groups. The effect of four different diets on life cycle of S. longipalpa was studied to determine the effect of them on the lifetime of each nymphal stage.
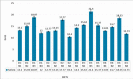
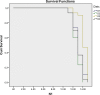
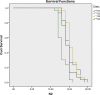
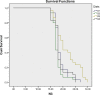
Results: The diets significantly affected on growth and development of immature life stages of S. longipalpa. Based on introduced diets to the cockroache populations, total immature life cycle was 54, 58, 60 and 66 d for diets 2,4,1, and 3 relatively. However, the overall lifetime of S. longipalpa in average was about 225 days.
Conclusion: As far as urban pest control is concerned, the result of this study will facilitate any operational programs for control of S. longipalpa. Among the different tested diets, diets 2 and 4 with less duration would be recommended for rearing of S. longipalpa in laboratory condition.
Keywords: Diet; Iran; Lifetime; Supella longipalpa.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endosymbiont and gut bacterial communities of the brown-banded cockroach, Supella longipalpa.PeerJ. 2024 Mar 19;12:e17095. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17095. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38525276 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on the Insecticide Resistance of Three Species of Cockroaches (Blattodea: Blattidae) in Iran.J Econ Entomol. 2019 Feb 12;112(1):1-10. doi: 10.1093/jee/toy247. J Econ Entomol. 2019. PMID: 30137353 Review.
-
Biocontrol of the Brown-Banded Cockroach, Supella longipalpa F. (Blattaria: Blattellidae), with Entomopathogenic Fungus, Metharhizium anisopliae.J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2016 Jan 6;10(3):335-46. eCollection 2016 Sep. J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2016. PMID: 27308292 Free PMC article.
-
The First Report of Drug Resistant Bacteria Isolated from the Brown-Banded Cockroach, Supella longipalpa, in Ahvaz, South-western Iran.J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2013 Dec 18;8(1):53-9. eCollection 2014. J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2013. PMID: 25629065 Free PMC article.
-
Contamination of cockroaches (Insecta: Blattaria) to medically fungi: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Mycol Med. 2017 Dec;27(4):427-448. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2017.04.012. Epub 2017 May 11. J Mycol Med. 2017. PMID: 28506564
References
-
- Bell WJ. (1969) Continuous and rhythmic reproductive cycle observed in Periplaneta americana (L.). Biol Bull Mar Biol Lab, Woods Hole. 137: 239–249.
-
- Cochran DG. (1983) Food and water consumption during the reproductive cycle of female German cockroaches. Ent Exp App. 34: 51–57.
-
- Durbin EJ, Cochran DG. (1985) Food and water deprivation effects on reproduction in female Blattella germanica. Ent Exp Appl. 37: 77–82.
-
- Hamilton RL, Schal C. (1988) Effects of dietary protein levels on reproduction and food consumption in the German cockroach (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae). Ann Entomol Soc Am. 81: 969–976.
-
- Kunkel JG. (1966) Development and the availability of food in the German cockroach, Blattella germanica (L). J Insect Physiol. 12: 227–235.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
