Variability in C-reactive protein is associated with cognitive impairment in women living with and without HIV: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 29063513
- PMCID: PMC6036635
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-017-0590-4
Variability in C-reactive protein is associated with cognitive impairment in women living with and without HIV: a longitudinal study
Abstract
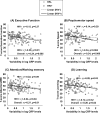
Despite the availability of effective antiretroviral therapies, cognitive impairment (CI) remains prevalent in HIV-infected (HIV+) individuals. Evidence from primarily cross-sectional studies, in predominantly male samples, implicates monocyte- and macrophage-driven inflammatory processes linked to HIV-associated CI. Thus, peripheral systemic inflammatory markers may be clinically useful biomarkers in tracking HIV-associated CI. Given sex differences in immune function, we focused here on whether mean and intra-individual variability in inflammatory marker-predicted CI in HIV+ and HIV- women. Seventy-two HIV+ (36 with CI) and 58 HIV- (29 with CI) propensity-matched women participating in the Women's Interagency HIV Study completed a neuropsychological battery once between 2009 and 2011, and performance was used to determine CI status. Analysis of 13 peripheral immune markers was conducted on stored biospecimens at three time points (7 and 3.5 years before neuropsychological data collection and concurrent with data collection). HIV+ women showed alterations in 8 immune markers compared to HIV- women. The strongest predictors of CI across HIV+ and HIV- women were lower mean soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor I (sTNFRI) levels, higher mean interleukin (IL)-6 levels, and greater variability in C-reactive protein (CRP) and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 (p values < 0.05). Stratified by HIV, the only significant predictor of CI was greater variability in CRP for both HIV+ and HIV- women (p values < 0.05). This variability predicted lower executive function, attention/working memory, and psychomotor speed in HIV+ but only learning in HIV- women (p values < 0.05). Intra-individual variability in CRP levels over time may be a good predictor of CI in predominately minority low-socioeconomic status midlife women.
Keywords: CRP; Cognition; HIV; Inflammation; Women.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monocyte Activation Is Associated With Worse Cognitive Performance in HIV-Infected Women With Virologic Suppression.J Infect Dis. 2017 Jan 1;215(1):114-121. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw506. Epub 2016 Oct 26. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 27789726 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin and interleukin-6, but not adipose tissue, are associated with worse neurocognitive function in HIV-infected men.Antivir Ther. 2015;20(2):235-44. doi: 10.3851/IMP2952. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Antivir Ther. 2015. PMID: 25810377 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 and C-Reactive Protein Levels and 9-Year Cognitive Decline in Community-Dwelling Older Women: The Women's Health and Aging Study II.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015 Jul;70(7):873-8. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glu132. Epub 2014 Aug 26. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25161214 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-associated executive dysfunction in the era of modern antiretroviral therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2018 May;40(4):357-376. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2017.1349879. Epub 2017 Jul 9. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2018. PMID: 28689493 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral levels of C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1β across the mood spectrum in bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis of mean differences and variability.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Oct;97:193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.07.014. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 34332041
Cited by
-
Cognition, Structural Brain Changes, and Systemic Inflammation in Adolescents Living With HIV on Antiretroviral Therapy.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2020 May 1;84(1):114-121. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002314. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2020. PMID: 32032303 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated aging in people living with HIV: The neuroimmune feedback model.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Feb 5;36:100737. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100737. eCollection 2024 Mar. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 38356933 Free PMC article.
-
A Pilot Investigation of the Association Between Vpr Amino Acid Substitutions and Peripheral Immune Marker Levels in People With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Implications for Neurocognitive Impairment.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Feb 27;11(3):ofae111. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae111. eCollection 2024 Mar. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38524224 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific associations between cerebrospinal fluid inflammatory marker levels and cognitive function in antiretroviral treated people living with HIV in rural Uganda.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Mar;93:111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.021. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 33359628 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Objectively-Measured Physical Activity and Cognitive Functioning in Middle-Aged and Older People Living with HIV.AIDS Behav. 2023 Apr;27(4):1199-1210. doi: 10.1007/s10461-022-03857-5. Epub 2022 Sep 27. AIDS Behav. 2023. PMID: 36163604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson AM, Fennema-Notestine C, Umlauf A, Taylor MJ, Clifford DB, Marra CM, Collier AC, Gelman BB, McArthur JC, McCutchan JA, Simpson DM, Morgello S, Grant I, Letendre SL. CSF biomarkers of monocyte activation and chemotaxis correlate with magnetic resonance spectroscopy metabolites during chronic HIV disease. J Neurovirol. 2015a;21:559–67. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson AM, Harezlak J, Bharti A, Mi D, Taylor MJ, Daar ES, Schifitto G, Zhong J, Alger JR, Brown MS, Singer EJ, Campbell TB, McMahon DD, Buchthal S, Cohen R, Yiannoutsos C, Letendre SL, Navia BA. Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers Predict Cerebral Injury in HIV-Infected Individuals on Stable Combination Antiretroviral Therapy. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015b;69:29–35. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antinori A, Arendt G, Becker JT, Brew BJ, Byrd DA, Cherner M, Clifford DB, Cinque P, Epstein LG, Goodkin K, Gisslen M, Grant I, Heaton RK, Joseph J, Marder K, Marra CM, McArthur JC, Nunn M, Price RW, Pulliam L, Robertson KR, Sacktor N, Valcour V, Wojna VE. Updated research nosology for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology. 2007;69:1789–99. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avison MJ, Nath A, Greene-Avison R, Schmitt FA, Greenberg RN, Berger JR. Neuroimaging correlates of HIV-associated BBB compromise. J Neuroimmunol. 2004;157:140–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI103397/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI082151/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD055892/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 MH098759/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103408/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH098798/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

