The eIF2-alpha kinase HRI: a potential target beyond the red blood cell
- PMID: 29063813
- PMCID: PMC5761058
- DOI: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1397133
The eIF2-alpha kinase HRI: a potential target beyond the red blood cell
Abstract
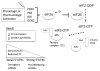
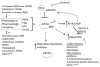
The eIF2α kinase heme-regulated inhibitor (HRI) is one of four well-described kinases that phosphorylate eIF2α in response to various cell stressors, resulting in reduced ternary complex formation and attenuation of mRNA translation. Although HRI is well known for its role as a heme sensor in erythroid progenitors, pharmacologic activation of HRI has been demonstrated to have anti-cancer activity across a wide range of tumor sub-types. Here, the potential of HRI activators as novel cancer therapeutics is explored. Areas covered: We provide an introduction to eIF2 signaling pathways in general, and specifically review data on the eIF2α kinase HRI in erythroid and non-erythroid cells. We review aspects of targeting eIF2 signaling in cancer and highlight promising data using HRI activators against tumor cells. Expert opinion: Pharmacologic activation of HRI inhibits tumor growth as a single agent without appreciable toxicity in vivo. The ability of HRI activators to provide direct and sustained eIF2α phosphorylation without inducing oxidative stress or broad eIF2α kinase activation may be especially advantageous for tolerability. Combination therapy with established therapeutics may further augment anti-cancer activity to overcome disease resistance.
Keywords: Cancer; ER stress; HRI; eIF2; translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties. Peer reviewers on this manuscript have no relevant financial or other relationships to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Spilka R, Ernst C, Mehta AK, et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factors in cancer development and progression. Cancer Lett. 2013;340(1):9–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
