Endocrine Disruptors Leading to Obesity and Related Diseases
- PMID: 29064461
- PMCID: PMC5664782
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph14101282
Endocrine Disruptors Leading to Obesity and Related Diseases
Abstract
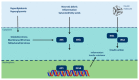
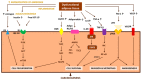
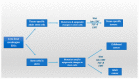
The review aims to comprehensively present the impact of exposure to endocrine disruptors (EDs) in relation to the clinical manifestation of obesity and related diseases, including diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular diseases, carcinogenesis and infertility. EDs are strong participants in the obesity epidemic scenery by interfering with cellular morphological and biochemical processes; by inducing inflammatory responses; and by presenting transcriptional and oncogenic activity. Obesity and lipotoxicity enhancement occur through reprogramming and/or remodeling of germline epigenome by exposure to EDs. Specific population groups are vulnerable to ED exposure due to current dietary and environmental conditions. Obesity, morbidity and carcinogenicity induced by ED exposure are an evolving reality. Therefore, a new collective strategic approach is deemed essential, for the reappraisal of current global conditions pertaining to energy management.
Keywords: carcinogenesis; cardiovascular diseases; diabetes mellitus; endocrine disruptors; infertility; metabolic syndrome; obesity; pesticides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization: Obesity and Overweight. [(accessed on 3 August 2017)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
-
- OECD Obesity Update. [(accessed on 3 August 2017)];2017 Available online: http://www.oecd.org/health/obesity-update.htm.
-
- Environment and Climate Research Programme of DG XII of the European Commission . EUR 17549, The European Workshop on the Impact of Endocrine Disrupters on Human Health and Wildlife, Report of Proceedings Weybridge, UK, 1996. Environment and Climate Research Programme of DG XII of the European Commission; Weybridge, UK: 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

