Highly Specific Binding on Antifouling Zwitterionic Polymer-Coated Microbeads as Measured by Flow Cytometry
- PMID: 29064669
- PMCID: PMC5682608
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b09725
Highly Specific Binding on Antifouling Zwitterionic Polymer-Coated Microbeads as Measured by Flow Cytometry
Abstract
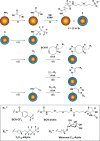
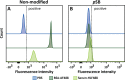
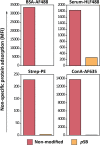
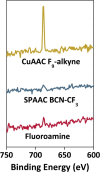
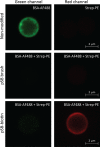
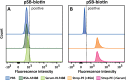
Micron- and nano-sized particles are extensively used in various biomedical applications. However, their performance is often drastically hampered by the nonspecific adsorption of biomolecules, a process called biofouling, which can cause false-positive and false-negative outcomes in diagnostic tests. Although antifouling coatings have been extensively studied on flat surfaces, their use on micro- and nanoparticles remains largely unexplored, despite the widespread experimental (specifically, clinical) uncertainties that arise because of biofouling. Here, we describe the preparation of magnetic micron-sized beads coated with zwitterionic sulfobetaine polymer brushes that display strong antifouling characteristics. These coated beads can then be equipped with recognition elements of choice, to enable the specific binding of target molecules. First, we present a proof of principle with biotin-functionalized beads that are able to specifically bind fluorescently labeled streptavidin from a complex mixture of serum proteins. Moreover, we show the versatility of the method by demonstrating that it is also possible to functionalize the beads with mannose moieties to specifically bind the carbohydrate-binding protein concanavalin A. Flow cytometry was used to show that thus-modified beads only bind specifically targeted proteins, with minimal/near-zero nonspecific protein adsorption from other proteins that are present. These antifouling zwitterionic polymer-coated beads, therefore, provide a significant advancement for the many bead-based diagnostic and other biosensing applications that require stringent antifouling conditions.
Keywords: antifouling; biosensing; flow cytometry; microbead; sulfobetaine; zwitterionic polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficient and Tunable Three-Dimensional Functionalization of Fully Zwitterionic Antifouling Surface Coatings.Langmuir. 2016 Oct 11;32(40):10199-10205. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b02622. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Langmuir. 2016. PMID: 27687696
-
Systematic Comparison of Zwitterionic and Non-Zwitterionic Antifouling Polymer Brushes on a Bead-Based Platform.Langmuir. 2019 Feb 5;35(5):1181-1191. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01832. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Langmuir. 2019. PMID: 30265555 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular level studies on interfacial hydration of zwitterionic and other antifouling polymers in situ.Acta Biomater. 2016 Aug;40:6-15. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.02.030. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 26923530 Review.
-
Zwitterionic sulfobetaine polymer-immobilized surface by simple tyrosinase-mediated grafting for enhanced antifouling property.Acta Biomater. 2017 Oct 1;61:169-179. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.08.007. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28782724
-
Zwitterionic Polymers for Biomedical Applications: Antimicrobial and Antifouling Strategies toward Implantable Medical Devices and Drug Delivery.Langmuir. 2024 Nov 5;40(44):23125-23145. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c02664. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 39450830 Review.
Cited by
-
Airway mucus in pulmonary diseases: Muco-adhesive and muco-penetrating particles to overcome the airway mucus barriers.Int J Pharm. 2023 Mar 5;634:122661. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.122661. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Int J Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36736964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Romantic Surfaces: A Systematic Overview of Stable, Biospecific, and Antifouling Zwitterionic Surfaces.Langmuir. 2019 Feb 5;35(5):1072-1084. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b03360. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Langmuir. 2019. PMID: 30620199 Free PMC article.
-
Modular Design for Proteins Assembling into Antifouling Coatings: Case of Gold Surfaces.Langmuir. 2023 Jul 11;39(27):9290-9299. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c00389. Epub 2023 Jun 27. Langmuir. 2023. PMID: 37366321 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Antifouling Mechanisms on Different Chain Densities of Zwitterionic Polymers.Molecules. 2022 Oct 31;27(21):7394. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217394. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364221 Free PMC article.
-
The Effective Charge of Low-Fouling Polybetaine Brushes.Langmuir. 2025 Jun 24;41(24):15307-15318. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5c00759. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Langmuir. 2025. PMID: 40491024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morgan E.; Varro R.; Sepulveda H.; Ember J. A.; Apgar J.; Wilson J.; Lowe L.; Chen R.; Shivraj L.; Agadir A.; Campos R.; Ernst D.; Gaur A. Cytometric Bead Array: A Multiplexed Assay Platform with Applications in Various Areas of Biology. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 110, 252–266. 10.1016/j.clim.2003.11.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arruebo M.; Fernández-Pacheco R.; Ibarra M. R.; Santamaría J. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Nano Today 2007, 2, 22–32. 10.1016/s1748-0132(07)70084-1. - DOI
-
- Mornet S.; Vasseur S.; Grasset F.; Veverka P.; Goglio G.; Demourgues A.; Portier J.; Pollert E.; Duguet E. Magnetic Nanoparticle Design for Medical Applications. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2006, 34, 237–247. 10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2005.11.010. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

