Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Antibiotic CJ-16,264, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Designed Analogues, and Discovery of Highly Potent and Simpler Antibacterial Agents
- PMID: 29064688
- PMCID: PMC5826612
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b08749
Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Antibiotic CJ-16,264, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Designed Analogues, and Discovery of Highly Potent and Simpler Antibacterial Agents
Abstract
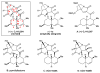
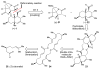
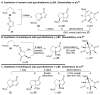
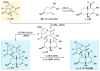
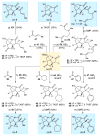
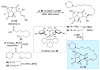
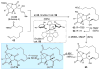
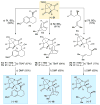
An improved and enantioselective total synthesis of antibiotic CJ-16,264 through a practical kinetic resolution and an iodolactonization reaction to form the iodo pyrrolizidinone fragment of the molecule is described. A series of racemic and enantiopure analogues of CJ-16,264 was designed and synthesized through the developed synthetic technologies and tested against drug-resistant bacterial strains. These studies led to interesting structure-activity relationships and the identification of a number of simpler, and yet equipotent, or even more potent, antibacterial agents than the natural product, thereby setting the foundation for further investigations in the quest for new anti-infective drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Total Synthesis and Structural Revision of Antibiotic CJ-16,264.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015 Aug 3;54(32):9203-8. doi: 10.1002/anie.201504337. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2015. PMID: 26096055 Free PMC article.
-
New pyrrolizidinone antibiotics CJ-16,264 and CJ-16,367.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2001 Nov;54(11):917-25. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.54.917. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2001. PMID: 11827034
-
New antibacterial agents derived from the DNA gyrase inhibitor cyclothialidine.J Med Chem. 2004 Mar 11;47(6):1487-513. doi: 10.1021/jm0310232. J Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 14998336
-
Synthesis and antibacterial activity of a new series of 3-[3-(substituted phenyl)-1-isonicotinoyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl]-2H-chromen-2-one derivatives.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2009 Jun;342(6):361-6. doi: 10.1002/ardp.200800156. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2009. PMID: 19475595
-
Challenges in the synthesis of a unique mono-carboxylic acid antibiotic, (+)-zincophorin.Nat Prod Rep. 2009 Apr;26(4):560-71. doi: 10.1039/b821450f. Nat Prod Rep. 2009. PMID: 19642422 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tricyclic Fused Lactams by Mukaiyama Cyclisation of Phthalimides and Evaluation of their Biological Activity.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 21;12(1):9. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010009. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36671210 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Mining and Assembly-Line Biosynthesis of the UCS1025A Pyrrolizidinone Family of Fungal Alkaloids.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Feb 14;140(6):2067-2071. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b00056. Epub 2018 Feb 2. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 29373009 Free PMC article.
-
Scalable Access to Arylomycins via C-H Functionalization Logic.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Feb 14;140(6):2072-2075. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b00087. Epub 2018 Feb 6. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 29381350 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sugie Y, Hirai H, Kachi-Tonai H, Kim YJ, Kojima Y, Shiomi Y, Sugiura A, Sugiura A, Suzuki Y, Yoshikawa N, Brennan L, Duignan J, Huang LH, Sutcliffe J, Kojima N. J Antibiot. 2001;54:917–925. - PubMed
-
- Nogawa T, Kawatani M, Uramoto M, Okano A, Aono H, Futamura Y, Koshino H, Takahashi S, Osada H. J Antibiot. 2013;66:621–623. - PubMed
-
- Nakai R, Ogawa H, Asai A, Ando K, Agatsuma T, Matsumiya S, Akinaga S, Yamashita Y, Mizukami T. J Antibiot. 2000;53:294–296. - PubMed
- Agatsuma T, Akama T, Nara S, Matsumiya S, Nakai R, Ogawa H, Otaki S, Ikeda S-i, Saitoh Y, Kanda Y. Org Lett. 2002;4:4387–4390. - PubMed
- Lambert TH, Danishefsky SJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:426–427. - PubMed
- Hoye TR, Dvornikovs V. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:2550–2551. - PubMed
- de Figueiredo RM, Fröhlich R, Christmann M. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2007;46:2883–2886. - PubMed
- Sizova EP. PhD Dissertation. University of Minnesota; Minneapolis, MN: 2009. Second Generation Synthesis of UCS1025A. Synthetic Efforts Toward Total Syntheses of CJ-16,264 and Phomopsichalasin.
- Uchida K, Ogawa T, Yasuda Y, Mimura H, Fujimoto T, Fukuyama T, Wakimoto T, Asakawa T, Hamashima Y, Kan T. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2012;51:12850–12853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

