The Role of MDM2 in Promoting Genome Stability versus Instability
- PMID: 29065514
- PMCID: PMC5666895
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18102216
The Role of MDM2 in Promoting Genome Stability versus Instability
Abstract
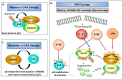
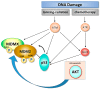
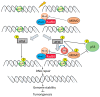
In cancer, the mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) is an oncoprotein that contributes to the promotion of cell growth, survival, invasion, and therapeutic resistance. The impact of MDM2 on cell survival versus cell death is complex and dependent on levels of MDM2 isoforms, p53 status, and cellular context. Extensive investigations have demonstrated that MDM2 protein-protein interactions with p53 and other p53 family members (p63 and p73) block their ability to function as transcription factors that regulate cell growth and survival. Upon genotoxic insults, a dynamic and intricately regulated DNA damage response circuitry is activated leading to release of p53 from MDM2 and activation of cell cycle arrest. What ensues following DNA damage, depends on the extent of DNA damage and if the cell has sufficient DNA repair capacity. The well-known auto-regulatory loop between p53-MDM2 provides an additional layer of control as the cell either repairs DNA damage and survives (i.e., MDM2 re-engages with p53), or undergoes cell death (i.e., MDM2 does not re-engage p53). Furthermore, the decision to live or die is also influenced by chromatin-localized MDM2 which directly interacts with the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex and inhibits DNA damage-sensing giving rise to the potential for increased genome instability and cellular transformation.
Keywords: DNA damage; MDM2; genome instability; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
 Activation =
Activation =  .
.Similar articles
-
Mdm2 affects genome stability independent of p53.Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 1;69(5):1697-701. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3732. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19244108 Review.
-
Pharmacologically Increasing Mdm2 Inhibits DNA Repair and Cooperates with Genotoxic Agents to Kill p53-Inactivated Ovarian Cancer Cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2015 Aug;13(8):1197-205. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0089. Epub 2015 May 11. Mol Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25964101 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Mdm2 and Mdmx in DNA repair.J Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Feb 1;9(1):69-73. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjw052. J Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27932484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Murine double minute 2: p53-independent roads lead to genome instability or death.Trends Biochem Sci. 2009 Jun;34(6):279-86. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.02.006. Epub 2009 May 15. Trends Biochem Sci. 2009. PMID: 19447627 Review.
-
[Multifunctionality of MDM2 protein and its role in genomic instability of cancer cells].Postepy Biochem. 2015;61(1):42-51. Postepy Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26281353 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Novel biomolecules in targeted cancer therapy: a new approach towards precision medicine.Med Oncol. 2023 Oct 7;40(11):323. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02168-6. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37804361 Review.
-
Functional role and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of the miR-590-3p/MDM2 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2023 May 4;23(1):396. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10861-y. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37138218 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic regressive trajectories in colorectal cancer: A new hallmark of oligo-metastatic disease?Transl Oncol. 2021 Aug;14(8):101131. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101131. Epub 2021 May 23. Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34034007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MDM2 Integrates Cellular Respiration and Apoptotic Signaling through NDUFS1 and the Mitochondrial Network.Mol Cell. 2019 May 2;74(3):452-465.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.012. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30879903 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of proteins by PROTACs and other strategies.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 Feb;10(2):207-238. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 32082969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

