Blood Vessel Extraction in Color Retinal Fundus Images with Enhancement Filtering and Unsupervised Classification
- PMID: 29065611
- PMCID: PMC5559979
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4897258
Blood Vessel Extraction in Color Retinal Fundus Images with Enhancement Filtering and Unsupervised Classification
Abstract
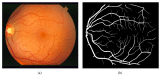
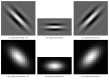
Retinal blood vessels have a significant role in the diagnosis and treatment of various retinal diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, arteriosclerosis, and hypertension. For this reason, retinal vasculature extraction is important in order to help specialists for the diagnosis and treatment of systematic diseases. In this paper, a novel approach is developed to extract retinal blood vessel network. Our method comprises four stages: (1) preprocessing stage in order to prepare dataset for segmentation; (2) an enhancement procedure including Gabor, Frangi, and Gauss filters obtained separately before a top-hat transform; (3) a hard and soft clustering stage which includes K-means and Fuzzy C-means (FCM) in order to get binary vessel map; and (4) a postprocessing step which removes falsely segmented isolated regions. The method is tested on color retinal images obtained from STARE and DRIVE databases which are available online. As a result, Gabor filter followed by K-means clustering method achieves 95.94% and 95.71% of accuracy for STARE and DRIVE databases, respectively, which are acceptable for diagnosis systems.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Segmenting retinal vessels with revised top-bottom-hat transformation and flattening of minimum circumscribed ellipse.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2019 Jul;57(7):1481-1496. doi: 10.1007/s11517-019-01967-2. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2019. PMID: 30903529
-
Blood Vessel Segmentation of Fundus Images by Major Vessel Extraction and Subimage Classification.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2015 May;19(3):1118-28. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2014.2335617. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2015. PMID: 25014980
-
An efficient retinal blood vessel segmentation in eye fundus images by using optimized top-hat and homomorphic filtering.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Apr;201:105949. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.105949. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 33567382
-
Blood vessel segmentation in color fundus images based on regional and Hessian features.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017 Aug;255(8):1525-1533. doi: 10.1007/s00417-017-3677-y. Epub 2017 May 4. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28474130 Review.
-
Automated techniques for blood vessels segmentation through fundus retinal images: A review.Microsc Res Tech. 2019 Feb;82(2):153-170. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23172. Epub 2019 Jan 5. Microsc Res Tech. 2019. PMID: 30614150 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Vessel Segmentation Based on Various Enhancement Techniques for Improvement of Vessel Intensity Profile.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 28;2022:7086632. doi: 10.1155/2022/7086632. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35800676 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Multiscale Gaussian-Matched Filter Using Neural Networks for the Segmentation of X-Ray Coronary Angiograms.J Healthc Eng. 2018 Apr 18;2018:5812059. doi: 10.1155/2018/5812059. eCollection 2018. J Healthc Eng. 2018. PMID: 29849999 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid approach for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy from fundus image exploiting deep features.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 4;9(9):e19625. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19625. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809795 Free PMC article.
-
Multiscale Joint Optimization Strategy for Retinal Vascular Segmentation.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 7;22(3):1258. doi: 10.3390/s22031258. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35162002 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Model Structure for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification.J Healthc Eng. 2020 Oct 13;2020:8840174. doi: 10.1155/2020/8840174. eCollection 2020. J Healthc Eng. 2020. PMID: 33110484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walter T., Klein J.-C. Segmentation of color fundus images of the human retina: detection of the optic disc and the vascular tree using morphological techniques. Medical Data Analysis. 2001. pp. 282–287.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

