Exploring the potential cost-effectiveness of precision medicine treatment strategies for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 29065744
- PMCID: PMC5918224
- DOI: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1390230
Exploring the potential cost-effectiveness of precision medicine treatment strategies for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Activated B-cell-like (ABC) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is associated with worse survival after standard rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (RCHOP) chemoimmunotherapy compared to germinal center B-cell-like (GCB) subtype. Preliminary evidence suggests that benefits from novel agents may vary by subtype. Hypothesizing that treatment stratified by DLBCL subtype could be potentially cost-effective, we developed micro-simulation models to compare three first-line treatment strategies: (1) standard RCHOP for all patients (2) subtype testing followed by RCHOP for GCB and novel treatment for ABC DLBCL, and (3) novel treatment for all patients. Based on phase 2 evidence, we used lenalidomide + RCHOP as a surrogate novel treatment. The subtype-based approach showed a favorable incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $15,015/quality-adjusted life year compared with RCHOP. Although our exploratory analyses demonstrated a wide range of conditions where subtype-based treatment remained cost-effective, data from phase 3 trials are needed to validate our models' findings and draw definitive conclusions.
Keywords: ABC DLBCL; Lymphoma; cost-effectiveness; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; subtype testing.
Figures
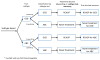
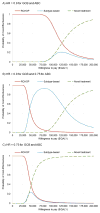
Comment in
-
The price of success-health economics of personalized diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treatment.Leuk Lymphoma. 2018 Jul;59(7):1517-1519. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1408088. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018. PMID: 29214866 No abstract available.
References
-
- Teras LR, DeSantis CE, Cerhan JR, Morton LM, Jemal A, Flowers CR. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA. J Clin. 2016 - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 2004;103:275–282. - PubMed
-
- Lenz G, Wright G, Dave S, et al. Gene expression signatures predict survival in diffuse large B cell lymphoma following rituximab and CHOP-like chemotherapy. Annals of Oncology. 2008;19:93–93.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
