Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in systemic sclerosis: results from the open-label period of a phase II randomised controlled trial (faSScinate)
- PMID: 29066464
- PMCID: PMC5867414
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211682
Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in systemic sclerosis: results from the open-label period of a phase II randomised controlled trial (faSScinate)
Abstract
Objectives: Assess the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) in a phase II study.
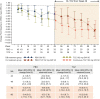
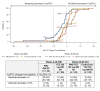
Methods: Patients with SSc were treated for 48 weeks in an open-label extension phase of the faSScinate study with weekly 162 mg subcutaneous tocilizumab. Exploratory end points included modified Rodnan Skin Score (mRSS) and per cent predicted forced vital capacity (%pFVC) through week 96.
Results: Overall, 24/44 (55%) placebo-tocilizumab and 27/43 (63%) continuous-tocilizumab patients completed week 96. Observed mean (SD (95% CI)) change from baseline in mRSS was -3.1 (6.3 (-5.4 to -0.9)) for placebo and -5.6 (9.1 (-8.9 to-2.4)) for tocilizumab at week 48 and -9.4 (5.6 (-8.9 to -2.4)) for placebo-tocilizumab and -9.1 (8.7 (-12.5 to -5.6)) for continuous-tocilizumab at week 96. Of patients who completed week 96, any decline in %pFVC was observed for 10/24 (42% (95% CI 22% to 63%)) placebo-tocilizumab and 12/26 (46% (95% CI 27% to 67%)) continuous-tocilizumab patients in the open-label period; no patients had >10% absolute decline in %pFVC. Serious infection rates/100 patient-years (95% CI) were 10.9 (3.0 to 27.9) with placebo and 34.8 (18.0 to 60.8) with tocilizumab during the double-blind period by week 48 and 19.6 (7.2 to 42.7) with placebo-tocilizumab and 0.0 (0.0 to 12.2) with continuous-tocilizumab during the open-label period.
Conclusions: Skin score improvement and FVC stabilisation in the double-blind period were observed in placebo-treated patients who transitioned to tocilizumab and were maintained in the open-label period. Safety data indicated increased serious infections in patients with SSc but no new safety signals with tocilizumab.
Trial registration number: NCT01532869; Results.
Keywords: DMARDs (biologic); interleukin-6; scleroderma; systemic sclerosis (SSc); tocilizumab; treatment.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: DK reports personal fees from Actelion, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Covis, CSL Behring, Corbus, Cytori, EMD Serono, Genentech/Roche, GSK, Inventiva, Medac, Sanofi-Aventis and UCB; grants from BMS, Bayer and Pfizer; stocks in Eicos Sciences, Inc, during the conduct of the study; and personal fees from Astra Zeneca outside the submitted work. CPD reports personal fees from Roche, Actelion, EMD Serono, Sanofi and Boehringer Ingelheim; grants and personal fees from GSK and Inventiva; and grants from CSL Behring during the conduct of the study. CJFL is an employee of Genentech. JMvL reports grants and personal fees from MSD and Genentech and personal fees from BMS, Eli Lilly and Pfizer outside the submitted work. MEA reports funding to Hospital Trust from Roche during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Actelion Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. YA has received research support and grants related to the submitted work from BMS, Roche/Genentech, Inventiva, Pfizer and Sanofi; consulting honoraria and personal fees related to the current work from Actelion, Bayer, Boehringer, Roche/Genentech, Galapagos, Inventiva, Medac, Pfizer, Sanofi, Servier and UCB; and personal fees outside the submitted work from Sandoz. JEP reports funding for the current trial by Roche. GR has received lecturer’s fees from Roche and Chugai outside the submitted work. UM-L is a speaker and advisor to Roche and Chugai related to the submitted work. HS is an employee of and has non-voting shares in Roche Products Limited. LB is an employee of Roche. JS is an employee of Genentech. AJ is an employee of Genentech, owns stock and options in Roche and owns a patent for subcutaneous tocilizumab. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
Response to: 'Effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab for the treatment of refractory systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease: a case series' by Narváez.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Nov;78(11):e124. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214477. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30352886 No abstract available.
-
Effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab for the treatment of refractory systemic sclerosis associated interstitial lung disease: a case series.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Nov;78(11):e123. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214449. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30352892 No abstract available.
-
Paradoxical pulmonary event under tocilizumab treatment for systemic sclerosis-associated usual interstitial pneumonia.Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 Feb;79(2):e22. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214747. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 30518522 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

