Citizen science provides a reliable and scalable tool to track disease-carrying mosquitoes
- PMID: 29066710
- PMCID: PMC5655677
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00914-9
Citizen science provides a reliable and scalable tool to track disease-carrying mosquitoes
Abstract
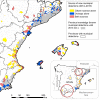
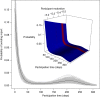
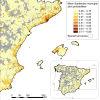
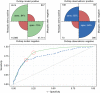
Recent outbreaks of Zika, chikungunya and dengue highlight the importance of better understanding the spread of disease-carrying mosquitoes across multiple spatio-temporal scales. Traditional surveillance tools are limited by jurisdictional boundaries and cost constraints. Here we show how a scalable citizen science system can solve this problem by combining citizen scientists' observations with expert validation and correcting for sampling effort. Our system provides accurate early warning information about the Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) invasion in Spain, well beyond that available from traditional methods, and vital for public health services. It also provides estimates of tiger mosquito risk comparable to those from traditional methods but more directly related to the human-mosquito encounters that are relevant for epidemiological modelling and scalable enough to cover the entire country. These results illustrate how powerful public participation in science can be and suggest citizen science is positioned to revolutionize mosquito-borne disease surveillance worldwide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


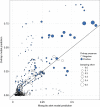
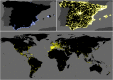
References
-
- Crowl TA, Crist TO, Parmenter RR, Belovsky G, Lugo AE. The spread of invasive species and infectious disease as drivers of ecosystem change. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008;6:238–246. doi: 10.1890/070151. - DOI
-
- Pimentel D, Zuniga R, Morrison D. Update on the environmental and economic costs associated with alien-invasive species in the United States. Ecol. Econ. 2005;52:273–288. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.10.002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

