An analysis of 3105 Medico Legal Cases at Tertiary Care Hospital, Rawalpindi
- PMID: 29067067
- PMCID: PMC5648966
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.334.11696
An analysis of 3105 Medico Legal Cases at Tertiary Care Hospital, Rawalpindi
Abstract
Background and objectives: Medico legal cases are essential component of medical practice and comprise most important constituent of emergencies. The reporting of such cases is imperative to recognize theirsocioeconomic burden on any country. The present study was conducted to scrutinize different categories of medico legal cases and characteristics of the victims at casualty department oftertiary care hospital Rawalpindi. The objective of the study was to find out the frequency ofvarious categories of medico legal cases and major characteristics ofvictims at tertiary care hospital, Rawalpindi.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study on 3105 registered cases in medico legal record of the casualty department of Benazir Bhutto hospital, Rawalpindi from January 2015 to December 2015. The hospital is located on the main road in densely populated central area of the city. The data wascollected on age, sex, month-wise distribution of various medico legal cases, weapon inflicting the injury, blunt trauma or physical assault, firearm injuries and road traffic accidents. The data thus obtained was analyzed using SPSS; observations were presented in tables and graphs.
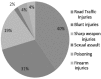
Results: Out of all 3105 registered medico legal cases, reported cases caused by Road Traffic Accident 1230 (40%) followed by blunt injury or physical assault 966 (32%) cases, 19% by sharp weapons, 5% by poisoning, and 4% by firearm injuries. In our study out of 3105 cases, almost three quarter of victims (73%) were below 30 years of age, with a decreasing frequency beyond this age, males were predominantly inflicted 2516(81%) as compared to females 589 (19%). The reported road traffic accidents cases from urban areas were high (74%) as compared to those from rural locality (37%). In cases of blunt trauma, sharp weapon injuries and firearm injuries, there was a huge preponderance of victims from rural areas (65%), (62%) and 61% respectively, with urban cases constituting less.
Conclusion: Road traffic injuries are one of the foremost causes of medico legal cases followed by blunt trauma and sharp weapon injuries. The emerging medico legal cases are neglected epidemic in most of the developing countries comprising a considerable public health problem.
Keywords: Assault; Blunt trauma; Injuries; Medico legal cases; Road Traffic Accidents.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures
References
-
- Tajammul N, Chaudhry TH, Hanif S, Bhatti MA. Profile of medico legal cases at Jinnah Hospital Lahore. Ann King Edward Med Uni. 2005;11(3):332–335. doi:10.21649/akemu.v11i3.1038.
-
- Sandeep KS, Ranjit TM, Deshpande VL, Dilip WR. Profile of Medico-Legal Cases at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Ahmednagar, Maharashtra. Indian J Forensic Med Pathol. 2015;8(4):113–115. doi:10.21088/ijfmp.0974.3383.8415.1.
-
- Singh P, Verma SK. Profile of Medico legal Cases Admitted at a Newly Established Rural Medical College Hospital of Central India. Medico-Legal Update. 2015;15(1):111–115. doi:10.5958/0974-1283.2015.00026.2.
-
- Siddappa SC, Datta A. A Study Pattern of Medico-legal Cases Treated at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Central Karnataka. Indian J Forensic Comm Med. 2015;2(4):193–197. doi:10.5958/2394-6776.2015.00002.8.
-
- Timsinha S, Kar SM, Baral MP, Ranjitkar M. Profile of Pattern of Medico-Legal Cases in the Casualty of A Teaching Hospital of Western Region of Nepal. J Indian Acad Forensic Med. 2015;37(1):46–49. doi:10.5958/0974-0848.2015.00010.X.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources