Pilot assessment of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors and trafficking pathways in recurrent and metastatic canine subcutaneous mast cell tumours
- PMID: 29067211
- PMCID: PMC5645839
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.66
Pilot assessment of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors and trafficking pathways in recurrent and metastatic canine subcutaneous mast cell tumours
Abstract
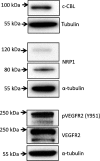
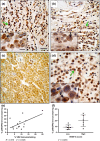
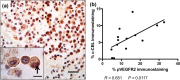
Canine subcutaneous mast cell tumour (scMCT) shows less aggressive biological behaviour than cutaneous MCT. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) is expressed by neoplastic cells in canine scMCT, but the relevance of this signalling pathway for disease pathobiology is not clear. The objective of this study was to quantify VEGF-A, VEGFR2, pVEGFR2, the VEGF co-receptor Neuropilin 1 (NRP-1) and the E3 ubiquitin protein ligase c-Cbl in canine scMCT, and to evaluate their association with disease outcome. Immunohistochemical staining for biomarkers was quantified from 14 cases of canine scMCT using manual and computer-assisted methods. Kaplan-Meier curves were generated for disease-free survival (DFS) and compared using Mantel-Cox log-rank analysis. Cases with high levels of neoplastic cell VEGFR2, pVEGFR2 or c-CBL immunoreactivity had significantly reduced DFS. All cases displayed neoplastic cells positive for VEGF-A, which was significantly associated with pVEGFR2 immunoreactivity. There were also significant positive correlations between VEGFR2 and pVEGFR2, and between c-CBL and pVEGFR2 levels. This pilot study demonstrates the potential utility of these markers in a subset of scMCT in dogs.
Keywords: Neuropilin‐1; VEGFR2; c‐CBL; dog.
Figures
References
-
- Adham S.A. & Coomber B.L. (2009) Glucose is a key regulator of VEGFR2/KDR in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 390, 130–135. - PubMed
-
- Bandi S.R., Brandts C., Rensinghoff M., Grundler R., Tickenbrock L., Kohler G. et al (2009) E3 ligase‐defective Cbl mutants lead to a generalized mastocytosis and myeloproliferative disease. Blood 114, 4197–4208. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

