First-in-human, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-dose escalation study of aducanumab (BIIB037) in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 29067304
- PMCID: PMC5651340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2016.06.002
First-in-human, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-dose escalation study of aducanumab (BIIB037) in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Aducanumab (BIIB037), a human monoclonal antibody selective for aggregated forms of amyloid beta, is being investigated as a disease-modifying treatment for Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled single ascending-dose study investigated the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of aducanumab in patients with mild-to-moderate AD. Eligible patients were sequentially randomized 6:2 to aducanumab (0.3, 1, 3, 10, 20, 30, and 60 mg/kg) or placebo.
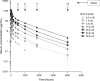
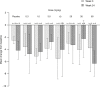
Results: The primary outcome was safety and tolerability. Doses ≤30 mg/kg were generally well tolerated with no severe or serious adverse events (SAEs). All three patients who received 60 mg/kg aducanumab developed SAEs of symptomatic amyloid-related imaging abnormalities, which completely resolved by weeks 8-15. Aducanumab Cmax, AUC0-last, and AUCinf increased in a dose-proportional manner.
Discussion: In this single-dose study, aducanumab demonstrated an acceptable safety and tolerability profile and linear PK at doses ≤30 mg/kg (clinicaltrials.govNCT01397539).
Keywords: Adverse events; Alzheimer's disease; Clinical trial; Monoclonal antibody; Pharmacokinetics.
Figures

References
-
- Alzheimer's Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2009. Available at: https://www.alz.co.uk/research/files/WorldAlzheimerReport.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2016.
-
- Hardy J., Selkoe D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J.A., Higgins G.A. Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 1992;256:184–185. - PubMed
-
- Villemagne V.L., Burnham S., Bourgeat P., Brown B., Ellis K.A., Salvado O. Amyloid ß deposition, neurodegeneration, and cognitive decline in sporadic Alzheimer's disease: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:357–367. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
