Multiple comorbid neuropathologies in the setting of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology and implications for drug development
- PMID: 29067320
- PMCID: PMC5651346
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2016.09.002
Multiple comorbid neuropathologies in the setting of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology and implications for drug development
Abstract
Dementia is often characterized as being caused by one of several major diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), cerebrovascular disease, Lewy body disease, or a frontotemporal degeneration. Failure to acknowledge that more than one entity may be present precludes attempts to understand interactive relationships. The clinicopathological studies of dementia demonstrate that multiple pathologic processes often coexist. How overlapping pathologic findings affect the diagnosis and treatment of clinical AD and other dementia phenotypes was the topic taken up by the Alzheimer's Association's Research Roundtable in October 2014. This review will cover the neuropathologic basis of dementia, provide clinical perspectives on multiple pathologies, and discuss therapeutics and biomarkers targeting overlapping pathologies and how these issues impact clinical trials.High prevalence of multiple pathologic findings among individuals with clinical diagnosis of AD suggests that new treatment strategies may be needed to effectively treat AD and other dementing illnesses.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease (AD); Cerebrovascular disease; Frontotemporal degeneration; Lewy body disease; TDP-43; Tau; α-Synuclein; β-amyloid.
Figures
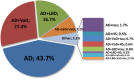
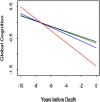
References
-
- Snowdon D.A. Aging and Alzheimer's disease: lessons from the Nun Study. Gerontologist. 1997;37:150–156. - PubMed
-
- Albert M.S., Dekosky S.T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H.H., Fox N.C. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:270–279. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hyman B.T., Trojanowski J.Q. Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer disease from the National Institute on Aging and the Reagan Institute Working Group on diagnostic criteria for the neuropathological assessment of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1997;56:1095–1097. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
