A case of total laparoscopic sigmoidectomy involving the use of needle forceps and transanal specimen extraction for sigmoid colon cancer
- PMID: 29067939
- PMCID: PMC5749203
- DOI: 10.4103/jmas.JMAS_110_17
A case of total laparoscopic sigmoidectomy involving the use of needle forceps and transanal specimen extraction for sigmoid colon cancer
Abstract
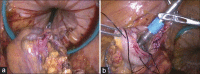
A 76-year-old male underwent endoscopic mucosal resection for a stage T1 tumour of the sigmoid colon. We performed laparoscopic sigmoidectomy through 5 ports using needlescopic instruments. The resected specimen was extracted from the abdominal cavity transanally. After attaching an anvil to the sigmoidal stump, the rectal stump was reclosed using an endoscopic linear stapler, and then, colorectal anastomosis was conducted using the double stapling technique. Performing transanal specimen extraction using needlescopic forceps improves aesthetic outcomes and reduces post-operative pain and the risk of abdominal incisional hernias. This method is an easy to introduce a form of reduced-port surgery because of its feasibility and conventional port arrangement. Hence, we consider that it is an option for minimally invasive surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Auyang ED, Santos BF, Enter DH, Hungness ES, Soper NJ. Natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery (NOTES(®)): A technical review. Surg Endosc. 2011;25:3135–48. - PubMed
-
- Champagne BJ, Papaconstantinou HT, Parmar SS, Nagle DA, Young-Fadok TM, Lee EC, et al. Single-incision versus standard multiport laparoscopic colectomy: A multicenter, case-controlled comparison. Ann Surg. 2012;255:66–9. - PubMed
-
- Ooi BS, Quah HM, Fu CW, Eu KW. Laparoscopic high anterior resection with natural orifice specimen extraction (NOSE) for early rectal cancer. Tech Coloproctol. 2009;13:61–4. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura A, Kawahara M, Suda K, Makino S, Kawachi Y, Nikkuni K, et al. Totally laparoscopic sigmoid colectomy with transanal specimen extraction. Surg Endosc. 2011;25:3459–63. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources