Synthesis, Structure, Surface and Antimicrobial Properties of New Oligomeric Quaternary Ammonium Salts with Aromatic Spacers
- PMID: 29068383
- PMCID: PMC6150277
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22111810
Synthesis, Structure, Surface and Antimicrobial Properties of New Oligomeric Quaternary Ammonium Salts with Aromatic Spacers
Abstract
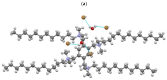
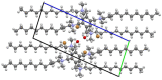
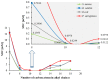
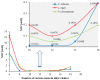
New dimeric, trimeric and tetrameric quaternary ammonium salts were accomplished by reaction of tertiary alkyldimethyl amines with appropriate bromomethylbenzene derivatives. A series of new cationic surfactants contain different alkyl chain lengths (C4-C18), aromatic spacers and different numbers of quaternary nitrogen atoms. The structure of the products was confirmed by spectral analysis (FT-IR, ¹H-NMR, 13C-NMR and 2D-NMR), mass spectroscopy (ESI-MS), elemental analysis, as well as PM5 semiempirical methods. Compound (21) was also analyzed using X-ray crystallography. Critical micelle concentration (CMC) of 1,4-bis-[N-(1-alkyl)-N,N-dimethylammoniummethyl]benzene dibromides (3-9) was determined to characterize the aggregation behavior. The antimicrobial properties of novel QACs (Quaternary Ammonium Salts) were examined to set their minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) values against fungi Aspergillus niger, Candida albicans, Penicillium chrysogenum and bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Keywords: CMC; antimicrobial properties; oligomeric surfactants; quaternary ammonium salts; rigid spacer; spectroscopy; synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Myers D. Surfactant Science and Technology. 3rd ed. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: New York, NY, USA: 2006.
-
- Rhein L.D. Surfactants in Personal Care Products and Decorative Cosmetics. 3rd ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2007.
-
- Karsa R.D. Surfactants in Polymers, Coatings, Inks, and Adhesives. 1st ed. Blackwell; Oxford, UK: 2003.
-
- Schramm L.L., Stasiuk E.N., Marangoni D.G. Surfactants and their applications. Annu. Rep. Prog. Chem. Sect. C Phys. Chem. 2003;99:3–48. doi: 10.1039/B208499F. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

