Effects of Black Raspberry Extract and Berry Compounds on Repair of DNA Damage and Mutagenesis Induced by Chemical and Physical Agents in Human Oral Leukoplakia and Rat Oral Fibroblasts
- PMID: 29068672
- PMCID: PMC7880227
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00242
Effects of Black Raspberry Extract and Berry Compounds on Repair of DNA Damage and Mutagenesis Induced by Chemical and Physical Agents in Human Oral Leukoplakia and Rat Oral Fibroblasts
Abstract
Black raspberries (BRB) have been shown to inhibit carcinogenesis in a number of systems, with most studies focusing on progression. Previously we reported that an anthocyanin-enriched black raspberry extract (BE) enhanced repair of dibenzo-[a,l]-pyrene dihydrodiol (DBP-diol)-induced DNA adducts and inhibited DBP-diol and DBP-diolepoxide (DBPDE)-induced mutagenesis in a lacI rat oral fibroblast cell line, suggesting a role for BRB in the inhibition of initiation of carcinogenesis. Here we extend this work to protection by BE against DNA adduct formation induced by dibenzo-[a,l]-pyrene (DBP) in a human oral leukoplakia cell line (MSK) and to a second carcinogen, UV light. Treatment of MSK cells with DBP and DBPDE led to a dose-dependent increase in DBP-DNA adducts. Treatment of MSK cells with BE after addition of DBP reduced levels of adducts relative to cells treated with DBP alone, and treatment of rat oral fibroblasts with BE after addition of DBPDE inhibited mutagenesis. These observations showed that BE affected repair of DNA adducts and not metabolism of DBP. As a proof of principle we also tested aglycones of two anthocyanins commonly found in berries, delphinidin chloride and pelargonidin chloride. Delphinidin chloride reduced DBP-DNA adduct levels in MSK cells, while PGA did not. These results suggested that certain anthocyanins can enhance repair of bulky DNA adducts. As DBP and its metabolites induced formation of bulky DNA adducts, we investigated the effects of BE on genotoxic effects of a second carcinogen that induces bulky DNA damage, UV light. UV irradiation produced a dose-dependent increase in cyclobutanepyrimidine dimer levels in MSK cells, and post-UV treatment with BE resulted in lower cyclobutanepyrimidine dimer levels. Post-UV treatment of the rat lacI cells with BE reduced UV-induced mutagenesis. Taken together, the results demonstrate that BE extract reduces bulky DNA damage and mutagenesis and support a role for BRB in the inhibition of initiation of carcinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


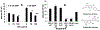

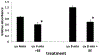
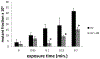
References
-
- Rao AV, and Snyder DM (2010) Raspberries and human health: a review. J. Agric. Food Chem 58, 3871–3883. - PubMed
-
- Seeram NP (2008) Berry fruits for cancer prevention: current status and future prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem 56, 630–635. - PubMed
-
- Stoner GD, and Wang LS (2012) Chemoprevention of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with berries. Top. Curr. Chem 329, 1–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

