Effects of TRPC1 on epithelial mesenchymal transition in human airway in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 29068985
- PMCID: PMC5671818
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008166
Effects of TRPC1 on epithelial mesenchymal transition in human airway in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
Background: We investigated the effects of TRPC1 on epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human airway in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Methods: A total of 94 patients who underwent lobectomy were selected and divided into COPD (49 cases) and control (45 cases) groups. Immunohistochemistry was applied to detect expression of E-cadherin and vimentin and TRPC1. Correlation of TRPC1 expression with E-cadherin and vimentin expression, and correlations of lung function indicators in COPD patients with expression of TRPC1, E-cadherin, and vimentin were analyzed. Human airway epithelial cells (16HBE) were used for cell experiments; and cigarette smoking extract (CSE) was adopted to establish the COPD model using TRPC1 recombinant plasmids and siRNA. Cells were assigned into the control, CSE, CSE + vector, CSE + TRPC1, CSE + si-NC, and CSE + si-TRPC1 groups. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot were implemented to detect expression of TRPC1, E-cadherin, and vimentin.
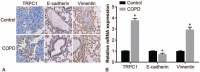
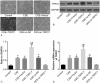
Results: Compared with the control group, expression of TRPC1 and vimentin significantly increased while expression of E-cadherin decreased in the COPD group, and protein expression of TRPC1 was positively correlated with the protein expression of vimentin but negatively correlated with the protein expression of E-cadherin. Patients exhibiting positive expression of TRPC1 had lower FEV1, FEV1%Pred, and FEV1/FVC, compared with the patients exhibiting negative expression of TRPC1. Compared with the control group, expression of TRPC1 and vimentin increased, whereas expression of E-cadherin decreased in the CSE, CSE + vector, CSE + TRPC1, and CSE + si-NC groups. Compared with the CSE and CSE + vector groups, the expression of TRPC1 and vimentin increased but the expression of E-cadherin decreased in the CSE + TRPC1 group. Compared with the CSE and CSE + si-NC groups, the expression of TRPC1 and vimentin decreased but the expression of E-cadherin increased in the CSE + si-TRPC1 group. No significant differences were observed among the CSE, CSE + vector and CSE + si-NC groups.
Conclusion: Overexpression of TRPC1 in COPD promoted EMT process and TRPC1 may be a new and interesting focus for COPD new treatment in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

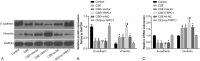
References
-
- To T, Zhu J, Larsen K, et al. Progression from asthma to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Is air pollution a risk factor? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016;194:429–38. - PubMed
-
- Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agusti AG, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013;187:347–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

