CDK1 interacts with iASPP to regulate colorectal cancer cell proliferation through p53 pathway
- PMID: 29069733
- PMCID: PMC5641076
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17794
CDK1 interacts with iASPP to regulate colorectal cancer cell proliferation through p53 pathway
Abstract
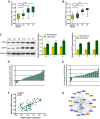
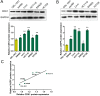
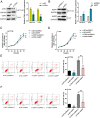
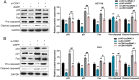
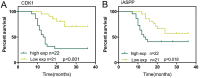
CDK1 (cyclin-dependent kinase 1) is a critical regulator of the G2-M checkpoint. CDK1 is considered a possible target for cancer treatment. In addition to CDK1, iASPP plays essential role in maintaining cancer cell proliferation. In the present study, we monitored the expression of CDK1 and iASPP at mRNA and protein levels in CRC tissues and cell lines; we also predicted that iASPP protein might interact with CDK1 protein. By performing GST pull-down assay and Co-IP assay, we confirmed the interaction of CDK1 and iASPP protein. In CRC cell lines, CDK1 interacted with iASPP to affect CRC cell proliferation and apoptosis; moreover, the p53 apoptosis pathway was involved in this progression. Taken together, we revealed that CDK1 and iASPP was up-regulated in CRC tissues and cell lines; CDK1 protein interacted with iASPP protein to affect CRC cell proliferation and apoptosis through the p53 apoptosis pathway. CDK1 and iASPP might serve as not only promising targets in CRC treatment, but also efficient prognostic markers. From the perspective of protein interactions, we provided a novel theoretical basis for targeted therapy of CRC.
Keywords: CDK1; cell proliferation; colorectal cancer; iASPP; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None for all authors.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Wolpin BM, Meyerhardt JA, Mamon HJ, Mayer RJ. Adjuvant treatment of colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:168–185. - PubMed
-
- Huang WW, Ko SW, Tsai HY, Chung JG, Chiang JH, Chen KT, Chen YC, Chen HY, Chen YF, Yang JS. Cantharidin induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer colo 205 cells through inhibition of CDK1 activity and caspase-dependent signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 2011;38:1067–1073. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro GI. Cyclin-dependent kinase pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1770–1783. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

