Induction of GD3/α1-adrenergic receptor/transglutaminase 2-mediated erythroid differentiation in chronic myelogenous leukemic K562 cells
- PMID: 29069780
- PMCID: PMC5641123
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20080
Induction of GD3/α1-adrenergic receptor/transglutaminase 2-mediated erythroid differentiation in chronic myelogenous leukemic K562 cells
Abstract
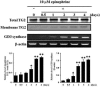
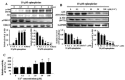
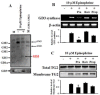
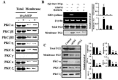
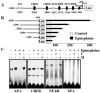
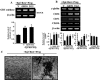
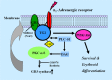
The disialic acid-containing glycosphingolipid GD3 recruited membrane transglutaminase 2 (TG2) as a signaling molecule for erythroid differentiation in human chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) K562 cells. The α1-adrenergic receptor (α1-AR)/TG2-mediated signaling pathway regulated GD3 functions, including gene expression and production, to differentiate CML K562 cells into erythroid lineage cells. Epinephrine, an AR agonist, increased membrane recruitment as well as GTP-photoaffinity of TG2, inducing GD3 synthase gene expression. Epinephrine activated PI3K/Akt signaling and GTPase downstream of TG2 activated Akt. The coupling of TG2 and GD3 production was specifically suppressed by prazosin (α1-AR antagonist), but not by propranolol (β-AR antagonist) or rauwolscine (α2-AR antagonist), indicating α1-AR specificity. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) experiment results indicated that the α1-AR/TG2-mediated signaling pathway activated PKCs α and δ to induce GD3 synthase gene expression. Transcription factors CREB, AP-1, and NF-κB regulated GD3 synthase gene expression during α1-AR-induced differentiation in CML K562 cells. In addition, GD3 synthase gene expression was upregulated in TG2-transfected cells via α1-AR with expression of erythroid lineage markers and benzidine-positive staining. α1-AR/TG2 signaling pathway-directed GD3 production is a crucial step in erythroid differentiation of K562 cells and GD3 interacts with α1-AR/TG2, inducing GD3/α1-AR/TG2-mediated erythroid differentiation. These results suggest that GD3, which acts as a membrane mediator of erythroid differentiation in CML cells, provides a therapeutic avenue for leukemia treatment.
Keywords: adrenergic receptor; erythroid differentiation; ganglioside GD3; human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cell; transglutaminase 2.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors did not declare any competing interests in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disialoganglioside GD3 synthase expression recruits membrane transglutaminase 2 during erythroid differentiation of the human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cells.Proteomics. 2008 Aug;8(16):3317-28. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200800153. Proteomics. 2008. PMID: 18690648
-
Overexpression of transglutaminase 2 accelerates the erythroid differentiation of human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cell line through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.FEBS Lett. 2004 Nov 19;577(3):361-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.10.031. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 15556610
-
Arsenic sulfide nanoformulation induces erythroid differentiation in chronic myeloid leukemia cells through degradation of BCR-ABL.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jul 22;14:5581-5594. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S207298. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31413564 Free PMC article.
-
Aclacinomycin A sensitizes K562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells to imatinib through p38MAPK-mediated erythroid differentiation.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 17;8(4):e61939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061939. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23613979 Free PMC article.
-
[Chemical control of cell differentiation of human myeloleukemia K562 cell line].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2000 Jan;120(1):104-12. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.120.1_104. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 10655786 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Remodeling the tumor immune microenvironment via siRNA therapy for precision cancer treatment.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 Sep;18(5):100852. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100852. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37920650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Transglutaminase 2 in Cancer: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 28;25(5):2797. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052797. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biological role and immunotherapy of gangliosides and GD3 synthase in cancers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 7;11:1076862. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1076862. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36824365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3'-sialyllactose targets cell surface protein, SIGLEC-3, and induces megakaryocyte differentiation and apoptosis by lipid raft-dependent endocytosis.Glycoconj J. 2020 Apr;37(2):187-200. doi: 10.1007/s10719-019-09902-1. Epub 2020 Jan 4. Glycoconj J. 2020. PMID: 31900723
-
Transcriptional Activation of Human GD3 Synthase (hST8Sia I) Gene in Curcumin-Induced Autophagy in A549 Human Lung Carcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 2;19(7):1943. doi: 10.3390/ijms19071943. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30004453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dohlman HG, Thorner J, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–88. - PubMed
-
- García-Sáinz JA. Alpha 1-adrenergic action: receptor subtypes, signal transduction and regulation. Cell Signal. 1993;5:539–47. - PubMed
-
- Hieble JP, Bylund DB, Clarke DE, Eikenburg DC, Langer SZ, Lefkowitz RJ, Minneman KP, Ruffolo RR, Jr, International Union of Pharmacology X. Recommendation for nomenclature of alpha 1-adrenoceptors: consensus update. Pharmacol Rev. 1995;47:267–70. - PubMed
-
- Minneman KP, Esbenshade TA. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1994;34:117–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

