Association of lower body mass index with increased glycemic variability in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study in China
- PMID: 29069856
- PMCID: PMC5641199
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17111
Association of lower body mass index with increased glycemic variability in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study in China
Abstract
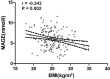
Previous studies have indicated that the pathogenesis of diabetes differs between obese and lean patients. We investigated whether newly diagnosed Chinese diabetic patients with different body mass indices (BMIs) have different glycemic variability, and we assessed the relationship between BMI and glycemic variability. This was a cross-sectional study that included 169 newly diagnosed and drug-naïve type 2 diabetic patients (mean age, 51.33 ± 9.83 years; 110 men). The clinical factors and results of the 75-g oral glucose tolerance test were all recorded. Glycemic variability was assessed using continuous glucose monitoring. Compared with overweight or obese patients (BMI ≥ 24 kg/m2), underweight or normal-weight patients (BMI < 24 kg/m2) had higher levels of blood glucose fluctuation parameters, particularly in terms of mean amplitude of glycemic excursion (MAGE 6.64 ± 2.38 vs. 5.67 ± 2.05; P = 0.007) and postprandial glucose excursions (PPGEs) (PPGE at breakfast, 7.72 ± 2.79 vs. 6.79 ± 2.40, P = 0.028; PPGE at lunch, 5.53 ± 2.70 vs. 5.07 ± 2.40, P = 0.285; PPGE at dinner, 5.96 ± 2.24 vs. 4.87 ± 2.50, P = 0.008). BMI was negatively correlated with glycemic variability (r = -0.243, P = 0.002). On multiple linear regression analyses, BMI (β = -0.231, P = 0.013) and Insulin Secretion Sensitivity Index-2 (β = -0.204, P = 0.048) were two independent predictors of glycemic variability. In conclusion, lower BMI was associated with increased glycemic variability, characterized by elevated PPGEs, in newly diagnosed Chinese type 2 diabetic patients.
Keywords: body mass index; continuous glucose monitoring; glycemic variability; obesity; postprandial glucose excursion.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- A mass survey of diabetes mellitus in a population of 300,000 in 14 provinces and municipalities in China. [Article in. Chinese] Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 1981;20:678–683. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, Xu M, Li Y, Hu N, et al. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 2013;310:948–959. - PubMed
-
- He J, Gu D, Wu X, Reynolds K, Duan X, Yao C, Wang J, Chen CS, Chen J, Wildman RP, Klag MJ, Whelton PK. Major causes of death among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1124–1134. - PubMed
-
- Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009;301:2129–2140. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

