Cleavable PEGylation: a strategy for overcoming the "PEG dilemma" in efficient drug delivery
- PMID: 29069920
- PMCID: PMC8812578
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1388451
Cleavable PEGylation: a strategy for overcoming the "PEG dilemma" in efficient drug delivery
Abstract
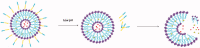
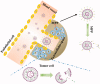
To prolong the circulation time of drug, PEGylation has been widely used via the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, thereby providing new hope for better treatment. However, PEGylation also brings the "PEG dilemma", which is difficult for the cellular absorption of drugs and subsequent endosomal escape. As a result, the activity of drugs is inevitably lost after PEG modification. To achieve successful drug delivery for effective treatment, the crucial issue associated with the use of PEG-lipids, that is, "PEG dilemma" must be addressed. In this paper, we introduced the development and application of nanocarriers with cleavable PEGylation, and discussed various strategies for overcoming the PEG dilemma. Compared to the traditional ones, the vehicle systems with different environmental-sensitive PEG-lipids were discussed, which cleavage can be achieved in response to the intracellular as well as the tumor microenvironment. This smart cleavable PEGylation provides us an efficient strategy to overcome "PEG dilemma", thereby may be a good candidate for the cancer treatment in future.
Keywords: PEGylation; cleavable PEG; drug delivery; nanocarriers; strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest. The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bae Y, Kataoka K. (2009). Intelligent polymeric micelles from functional poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(amino acid) block copolymers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:768–84. - PubMed
-
- Basile L, Passirani C, Huynh NT, et al. (2012). Serum-stable, long-circulating paclitaxel-loaded colloidal carriers decorated with a new amphiphilic PEG derivative. Int J Pharm 426:231–8. - PubMed
-
- Bian X, Shen F, Chen Y, et al. (2010). PEGylation of alpha-momorcharin: synthesis and characterization of novel anti-tumor conjugates with therapeutic potential. Biotechnol Lett 32:883–90. - PubMed
-
- Cai X, Dong H, Xia W, et al. (2011). Glutathione-mediated shedding of PEG layers based on disulfide-linked catiomers for DNA delivery. J Mater Chem 21:14639–45.
-
- Cai X, Dong C, Dong H, et al. (2012). Effective gene delivery using stimulus-responsive catiomer designed with redox-sensitive disulfide and acid-labile imine linkers. Biomacromolecules 13:1024–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
