Phosphorylation of Arabidopsis MAP Kinase Phosphatase 1 (MKP1) Is Required for PAMP Responses and Resistance against Bacteria
- PMID: 29070514
- PMCID: PMC5717735
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.17.01152
Phosphorylation of Arabidopsis MAP Kinase Phosphatase 1 (MKP1) Is Required for PAMP Responses and Resistance against Bacteria
Abstract
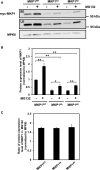
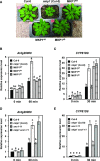
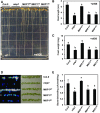
Plants perceive potential pathogens via the recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) by surface-localized pattern recognition receptors, which initiates a series of intracellular responses that ultimately limit bacterial growth. PAMP responses include changes in intracellular protein phosphorylation, including the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades. MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs), such as Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) MKP1, are important negative regulators of MAPKs and play a crucial role in controlling the intensity and duration of MAPK activation during innate immune signaling. As such, the mkp1 mutant lacking MKP1 displays enhanced PAMP responses and resistance against the virulent bacterium Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato DC3000. Previous in vitro studies showed that MKP1 can be phosphorylated and activated by MPK6, suggesting that phosphorylation may be an important mechanism for regulating MKP1. We found that MKP1 was phosphorylated during PAMP elicitation and that phosphorylation stabilized the protein, resulting in protein accumulation after elicitation. MKP1 also can be stabilized by the proteasome inhibitor MG132, suggesting that MKP1 is constitutively degraded through the proteasome in the resting state. In addition, we investigated the role of MKP1 posttranslational regulation in plant defense by testing whether phenotypes of the mkp1 Arabidopsis mutant could be complemented by expressing phosphorylation site mutations of MKP1. The phosphorylation of MKP1 was found to be required for some, but not all, of MKP1's functions in PAMP responses and defense against bacteria. Together, our results provide insight into the roles of phosphorylation in the regulation of MKP1 during PAMP signaling and resistance to bacteria.
© 2017 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis MAP Kinase Phosphatase 1 (AtMKP1) negatively regulates MPK6-mediated PAMP responses and resistance against bacteria.Plant J. 2011 Jul;67(2):258-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04588.x. Epub 2011 May 9. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21447069
-
Genetic dissection of Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1-dependent PAMP-induced transcriptional responses.J Exp Bot. 2017 Nov 2;68(18):5207-5220. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx335. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 29045691 Free PMC article.
-
MAP kinase phosphatase1 and protein tyrosine phosphatase1 are repressors of salicylic acid synthesis and SNC1-mediated responses in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2009 Sep;21(9):2884-97. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.067678. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Plant Cell. 2009. PMID: 19789277 Free PMC article.
-
MAP kinase signalling: interplays between plant PAMP- and effector-triggered immunity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Aug;75(16):2981-2989. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2839-3. Epub 2018 May 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29789867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MAPK phosphatases as novel targets for rheumatoid arthritis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008 Jul;12(7):795-808. doi: 10.1517/14728222.12.7.795. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008. PMID: 18554149 Review.
Cited by
-
CaMPK9 increases the stability of CaWRKY40 transcription factor which triggers defense response in chickpea upon Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. ciceri Race1 infection.Plant Mol Biol. 2019 Jul;100(4-5):411-431. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00868-0. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Plant Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30953279
-
Plant-exuded chemical signals induce surface attachment of the bacterial pathogen Pseudomonas syringae.PeerJ. 2023 Mar 27;11:e14862. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14862. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37009160 Free PMC article.
-
A dual-specificity phosphatase, MAP kinase phosphatase 1, positively regulates blue light-mediated seedling development in Arabidopsis.Planta. 2021 May 31;253(6):131. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03649-6. Planta. 2021. PMID: 34057637
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 controls broad spectrum disease resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana through diverse mechanisms of immune activation.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Mar 21;15:1374194. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1374194. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38576784 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatase NtPP2C2b and MAP kinase NtMPK4 act in concert to modulate nicotine biosynthesis.J Exp Bot. 2021 Feb 27;72(5):1661-1676. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa568. J Exp Bot. 2021. PMID: 33258946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson JC, Bartels S, González Besteiro MA, Shahollari B, Ulm R, Peck SC (2011) Arabidopsis MAP Kinase Phosphatase 1 (AtMKP1) negatively regulates MPK6-mediated PAMP responses and resistance against bacteria. Plant J 67: 258–268 - PubMed
-
- Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gómez-Gómez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415: 977–983 - PubMed
-
- Bartels S, González Besteiro MA, Lang D, Ulm R (2010) Emerging functions for plant MAP kinase phosphatases. Trends Plant Sci 15: 322–329 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

