Optimization of Experimental Parameters in Data-Independent Mass Spectrometry Significantly Increases Depth and Reproducibility of Results
- PMID: 29070702
- PMCID: PMC5724188
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.RA117.000314
Optimization of Experimental Parameters in Data-Independent Mass Spectrometry Significantly Increases Depth and Reproducibility of Results
Abstract
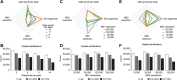
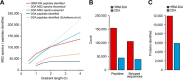
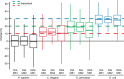
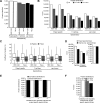
Comprehensive, reproducible and precise analysis of large sample cohorts is one of the key objectives of quantitative proteomics. Here, we present an implementation of data-independent acquisition using its parallel acquisition nature that surpasses the limitation of serial MS2 acquisition of data-dependent acquisition on a quadrupole ultra-high field Orbitrap mass spectrometer. In deep single shot data-independent acquisition, we identified and quantified 6,383 proteins in human cell lines using 2-or-more peptides/protein and over 7100 proteins when including the 717 proteins that were identified on the basis of a single peptide sequence. 7739 proteins were identified in mouse tissues using 2-or-more peptides/protein and 8121 when including the 382 proteins that were identified based on a single peptide sequence. Missing values for proteins were within 0.3 to 2.1% and median coefficients of variation of 4.7 to 6.2% among technical triplicates. In very complex mixtures, we could quantify 10,780 proteins and 12,192 proteins when including the 1412 proteins that were identified based on a single peptide sequence. Using this optimized DIA, we investigated large-protein networks before and after the critical period for whisker experience-induced synaptic strength in the murine somatosensory cortex 1-barrel field. This work shows that parallel mass spectrometry enables proteome profiling for discovery with high coverage, reproducibility, precision and scalability.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests: The authors R.B., T.G., O.M.B., and L.R. are employees of Biognosys AG (Zurich, Switzerland). Spectronaut is a trademark of Biognosys AG
Figures
References
-
- Aebersold R., and Mann M. (2003) Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422, 198–207 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

