Impact of pioglitazone and bradykinin type 1 receptor antagonist on type 2 diabetes in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice
- PMID: 29071111
- PMCID: PMC5598024
- DOI: 10.1002/osp4.117
Impact of pioglitazone and bradykinin type 1 receptor antagonist on type 2 diabetes in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice
Abstract
Aim: Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a major complication of obesity and a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. Antagonizing bradykinin type 1 receptor (B1R) improved body and tissue fat mass and reversed vascular and adipose tissue inflammation in a rat model of insulin resistance. This study aimed at evaluating further the role of B1R in a mouse model of T2D by comparing the antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects of the B1R antagonist SSR240612 (SSR) in adipose tissue with those of pioglitazone (TZD), an activator of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.
Methods: C57BL/6J mice were fed with high-fat diet (HFD) or standard diet (control) for 20 weeks. Yet, during the last 4 weeks, HFD-fed mice were administered SSR and TZD (10 mg kg-1 d-1 each) as monotherapy or combined therapy subcutaneously. The impact of treatments was measured on metabolic hormones levels (ELISA), adipose tissue inflammatory status and the expression of candidate genes involved in T2D (quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blot).
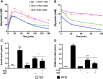
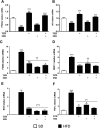
Results: SSR240612 and TZD treatments improved hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinaemia, insulin resistance, adipose tissue inflammation (expression of B1R, chemokine ligand 2, F4/80 and tumour necrosis factor) and modulated adipogenesis (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, adipocytes' protein 2 and CD40 expressions) in HFD-fed mice. Yet, SSR was more effective than TZD to reduce visceral fat mass and resistin. TZD/SSR combined treatment had an additive effect to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose intolerance.
Conclusion: Bradykinin type 1 receptor antagonism could represent a promising therapeutic tool in combination with TZD for the treatment of T2D, obesity and insulin resistance.
Keywords: Adipose tissue inflammation; PPARγ; bradykinin B1 receptor; obesity.
Figures



References
-
- Unger RH, Clark GO, Scherer PE, Orci L. Lipid homeostasis, lipotoxicity and the metabolic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1801: 209–214. - PubMed
-
- Yadav A, Kataria MA, Saini V, Yadav A. Role of leptin and adiponectin in insulin resistance. Clin Chim Acta 2013; 417: 80–84. - PubMed
-
- Caselli C. Role of adiponectin system in insulin resistance. Mol Genet Metab 2014; 113: 155–160. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
