Lower serotonin transporter binding in patients with cervical dystonia is associated with psychiatric symptoms
- PMID: 29071431
- PMCID: PMC5656503
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-017-0338-4
Lower serotonin transporter binding in patients with cervical dystonia is associated with psychiatric symptoms
Abstract
Background: Cervical dystonia (CD) is often accompanied by depressive symptoms, anxiety, and jerks/tremor. The dopamine transporter (DAT) binding is related with both depressive symptoms and jerks/tremor in CD. Serotonergic and dopaminergic systems are closely related. As serotonin is involved in the pathophysiology of psychiatric symptoms and jerks, we expected an altered serotoninergic system in CD. We hypothesized that CD is associated with reduced serotonin transporter (SERT) binding, more specific that SERT binding is lower in CD patients with psychiatric symptoms and/or jerks/tremor compared to those without, and to controls. The balance between SERT and DAT binding can be altered in different CD phenotypes.
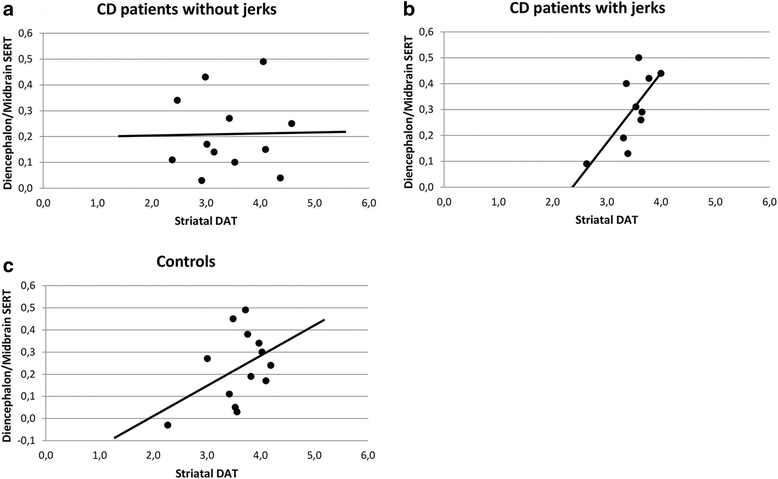
Results: In 23 CD patients and 14 healthy controls, SERT binding in the diencephalon/midbrain was assessed using [123I]FP-CIT SPECT, with a brain-dedicated system. The specific to non-specific binding ratio (binding potential; BPND) to SERT was the main outcome measure. There was a clear trend towards reduced SERT BPND in CD patients with psychiatric symptoms compared to those without (p = 0.05). There was no correlation between SERT binding and dystonia, jerks, or anxiety. There was a significant positive correlation between extrastriatal SERT and striatal DAT BPND in CD patients with jerks, but not in patients without jerks.
Conclusion: CD patients with psychiatric symptoms have lower SERT binding in the midbrain/diencephalon, while dystonia and jerks appear unrelated to SERT binding. The balance between extrastriatal SERT and striatal DAT binding is different in CD with and without jerks.
Keywords: Cervical dystonia; Depression; SPECT; Serotonin transporter (SERT).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Perlmutter JS, Mink JW. Dysfunction of dopaminergic pathways in dystonia. Adv Neurol. 2004;94:163–170. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials