Vigilance for threat accounts for inter-individual variation in physiological responses to adversity in rhesus macaques: A cognition × environment approach
- PMID: 29071705
- PMCID: PMC5690846
- DOI: 10.1002/dev.21572
Vigilance for threat accounts for inter-individual variation in physiological responses to adversity in rhesus macaques: A cognition × environment approach
Abstract
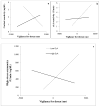
Early life adversity (ELA) can lead to poor health later in life. However, there is significant variation in outcomes, with some individuals displaying resilience even in the face of adversity. Using longitudinal data collected from free-ranging rhesus macaques between birth and 3 years, we examined whether individual variation in vigilance for threat, an early emerging attentional bias, can account for variation in long-term outcomes between individuals reared in similar environments. We found that ELA and vigilance during infancy interact to predict physiological dysregulation in Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) and Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) stress responses during juvenility. During high stress periods, High ELA juveniles with high vigilance exhibit less asymmetry than High ELA juveniles with low vigilance. This suggests that although increased vigilance is viewed as a negative consequence of ELA, it might also be a mechanism by which vulnerable individuals proactively buffer themselves from negative outcomes in unstable or threatening environments.
Keywords: asymmetry; cognitive bias; cortisol; early life adversity; rhesus macaque; salivary α-amylase.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Ali N, Pruessner JC. The salivary alpha amylase over cortisol ratio as a marker to assess dysrgulations of the stress systems. Physiology and Behavior. 2012;106:65–72. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Haim Y, Lamy D, Pergamin L, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, van IJzendoorn MH. Threat-related attentional bias in anxious and nonanxious individuals: A metaanalytic study. Psychological Bulletin. 2007;133:1–24. - PubMed
-
- Bauer AM, Quas JA, Boyce WT. Association between physiological reactivity and children’s behavior: Advantages of a multisystem approach. Journal of Developmental Behavioral Pediatrics. 2002;23:102–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

