Antituberculosis Drug-Induced Adverse Events in the Liver, Kidneys, and Blood: Clinical Profiles and Pharmacogenetic Predictors
- PMID: 29071720
- PMCID: PMC6099196
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.924
Antituberculosis Drug-Induced Adverse Events in the Liver, Kidneys, and Blood: Clinical Profiles and Pharmacogenetic Predictors
Abstract
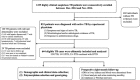
Antituberculosis drug-induced adverse drug reactions (ATD-ADRs) are increasing globally, and it is key to identify candidate ATD-ADRs loci for clinical management. We prospectively enrolled 1,235 highly suspicious tuberculosis (TB) inpatients to investigate the profiles and genetic risk factors of ATD-ADRs in the liver, kidneys, and blood. Overall, 644 subjects were eligible and genotyped for seven polymorphisms in drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporter genes. Clinical follow-up and blood analysis were performed regularly. We found that a notable rate of ATD-ADRs (incidence: 16.5%, drug intervention rate: 10.4%), mainly involving hepatotoxicity (10.6%) and leukopenia (3.3%) in western China. CYP2D6 rs1135840 and NUDT15 rs116855232 increased the risks of hepatotoxicity and leukopenia with an odds ratio of 2.52 and 4.97, respectively. Both variants showed excellent negative predictive values (93.7% and 98.1%, respectively) but moderate sensitivities (72.7% and 52.4%, respectively). These data provide new insight into ATD-ADRs in the Chinese population and may offer future leads for diagnosis and treatment.
© 2017 The Authors. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A prospective study on associations between superoxide dismutase gene polymorphisms and antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury in a Chinese Han population.J Gene Med. 2019 Oct;21(10):e3121. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3121. Epub 2019 Sep 4. J Gene Med. 2019. PMID: 31415712
-
Correlation between lncRNA AC079767.4 variants and liver injury from antituberculosis treatment in West China.J Infect Chemother. 2020 Jan;26(1):63-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Aug 9. J Infect Chemother. 2020. PMID: 31405785
-
Association of ABCC Gene Polymorphism With Susceptibility to Antituberculosis Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Western Han Patients With Tuberculosis.J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Mar;60(3):361-368. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1533. Epub 2019 Oct 24. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31648372
-
Diagnostic accuracy of NUDT15 gene variants for thiopurine-induced leukopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Sep;135:102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.07.021. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30048756
-
Pharmacokinetics of isoniazid: The good, the bad, and the alternatives.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019 May;116S:S66-S70. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2019.04.012. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019. PMID: 31076322 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress of Pharmacogenomics in Drug-Induced Liver Injury.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 6;12:735260. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.735260. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34552491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma metabolomic and lipidomic alterations associated with anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 24;13:1044808. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1044808. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36386176 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphisms in PXR and NF-κB1 influence susceptibility to anti-tuberculosis drug-induced liver injury.PLoS One. 2019 Sep 6;14(9):e0222033. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222033. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31490979 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effectiveness of Silymarin in the Prevention of Anti-tuberculosis Drug-induced Hepatotoxicity: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.Int J Prev Med. 2023 Apr 26;14:48. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.ijpvm_81_22. eCollection 2023. Int J Prev Med. 2023. PMID: 37351038 Free PMC article.
-
CYP2D6 genetic polymorphisms in Saudi systemic lupus erythematosus patients: A cross-sectional study.Saudi Med J. 2023 Mar;44(3):237-245. doi: 10.15537/smj.2023.44.3.20220581. Saudi Med J. 2023. PMID: 36940959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report 2016. Geneva: World Health Organization. <http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/> (2016) Accessed 13 October 2016.
-
- Sharma, S.K. et al Safety of 3 different reintroduction regimens of antituberculosis drugs after development of antituberculosis treatment‐induced hepatotoxicity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 50, 833–839 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Yamada, S. et al Genetic variation in carboxylesterase genes and susceptibility to isoniazid‐induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacogenom. J. 10, 524–536 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Fernandez‐Villar, A. et al Isoniazid hepatotoxicity among drug users: the role of hepatitis C. Clin. Infect. Dis. 36, 293–298 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials