Impaired excitation-contraction coupling in muscle fibres from the dynamin2R465W mouse model of centronuclear myopathy
- PMID: 29071728
- PMCID: PMC5730838
- DOI: 10.1113/JP274990
Impaired excitation-contraction coupling in muscle fibres from the dynamin2R465W mouse model of centronuclear myopathy
Abstract
Key points: Dynamin 2 is a ubiquitously expressed protein involved in membrane trafficking processes. Mutations in the gene encoding dynamin 2 are responsible for a congenital myopathy associated with centrally located nuclei in the muscle fibres. Using muscle fibres from a mouse model of the most common mutation responsible for this disease in humans, we tested whether altered Ca2+ signalling and excitation-contraction coupling contribute to muscle weakness. The plasma membrane network that carries the electrical excitation is moderately perturbed in the diseased muscle fibres. The excitation-activated Ca2+ input fluxes across both the plasma membrane and the membrane of the sarcoplasmic reticulum are defective in the diseased fibres, which probably contributes to muscle weakness in patients.
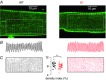
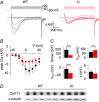
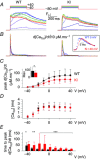
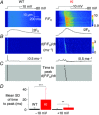
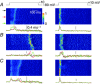
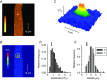
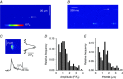
Abstract: Mutations in the gene encoding dynamin 2 (DNM2) are responsible for autosomal dominant centronuclear myopathy (AD-CNM). We studied the functional properties of Ca2+ signalling and excitation-contraction (EC) coupling in muscle fibres isolated from a knock-in (KI) mouse model of the disease, using confocal imaging and the voltage clamp technique. The transverse-tubule network organization appeared to be unaltered in the diseased fibres, although its density was reduced by ∼10% compared to that in control fibres. The density of Ca2+ current through CaV1.1 channels and the rate of voltage-activated sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release were reduced by ∼60% and 30%, respectively, in KI vs. control fibres. In addition, Ca2+ release in the KI fibres reached its peak value 10-50 ms later than in control ones. Activation of Ca2+ transients along the longitudinal axis of the fibres was more heterogeneous in the KI than in the control fibres, with the difference being exacerbated at intermediate membrane voltages. KI fibres exhibited spontaneous Ca2+ release events that were almost absent from control fibres. Overall, the results of the present study demonstrate that Ca2+ signalling and EC coupling exhibit a number of dysfunctions likely contributing to muscle weakness in DNM2-related AD-CNM.
Keywords: dynamin 2; excitation-contraction coupling; ryanodine receptor; sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release; skeletal muscle.
© 2017 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2017 The Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Agrawal PB, Pierson CR, Joshi M, Liu X, Ravenscroft G, Moghadaszadeh B, Talabere T, Viola M, Swanson LC, Haliloğlu G, Talim B, Yau KS, Allcock RJ, Laing NG, Perrella MA & Beggs AH (2014). SPEG interacts with myotubularin, and its deficiency causes centronuclear myopathy with dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Hum Genet 95, 218–226. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al‐Qusairi L, Weiss N, Toussaint A, Berbey C, Messaddeq N, Kretz C, Sanoudou D, Beggs AH, Allard B, Mandel JL, Laporte J, Jacquemond V & Buj‐Bello A (2009). T‐tubule disorganization and defective excitation‐contraction coupling in muscle fibers lacking myotubularin lipid phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 18763–18768. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bitoun M, Maugenre S, Jeannet PY, Lacène E, Ferrer X, Laforêt P, Martin JJ, Laporte J, Lochmüller H, Beggs AH, Fardeau M, Eymard B, Romero NB & Guicheney P (2005). Mutations in dynamin 2 cause dominant centronuclear myopathy. Nat Genet 37, 1207–1209. - PubMed
-
- Bitoun M, Bevilacqua JA, Prudhon B, Maugenre S, Taratuto AL, Monges S, Lubieniecki F, Cances C, Uro‐Coste E, Mayer M, Fardeau M, Romero NB & Guicheney P (2007). Dynamin 2 mutations cause sporadic centronuclear myopathy with neonatal onset. Ann Neurol 62, 666–670. - PubMed
-
- Böhm J, Biancalana V, Dechene ET, Bitoun M, Pierson CR, Schaefer E, Karasoy H, Dempsey MA, Klein F, Dondaine N, Kretz C, Haumesser N, Poirson C, Toussaint A, Greenleaf RS, Barger MA, Mahoney LJ, Kang PB, Zanoteli E, Vissing J, Witting N, Echaniz‐Laguna A, Wallgren‐Pettersson C, Dowling J, Merlini L, Oldfors A, Bomme Ousager L, Melki J, Krause A, Jern C, Oliveira AS, Petit F, Jacquette A, Chaussenot A, Mowat D, Leheup B, Cristofano M, Poza Aldea JJ, Michel F, Furby A, Llona JE, Van Coster R, Bertini E, Urtizberea JA, Drouin‐Garraud V, Béroud C, Prudhon B, Bedford M, Mathews K, Erby LA, Smith SA, Roggenbuck J, Crowe CA, Brennan Spitale A, Johal SC, Amato AA, Demmer LA, Jonas J, Darras BT, Bird TD, Laurino M, Welt SI, Trotter C, Guicheney P, Das S, Mandel JL, Beggs AH & Laporte J (2012). Mutation spectrum in the large GTPase dynamin 2, and genotype‐phenotype correlation in autosomal dominant centronuclear myopathy. Hum Mutat 33, 949–959. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

