Barbaloin inhibits ventricular arrhythmias in rabbits by modulating voltage-gated ion channels
- PMID: 29072259
- PMCID: PMC5843841
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2017.93
Barbaloin inhibits ventricular arrhythmias in rabbits by modulating voltage-gated ion channels
Abstract
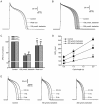
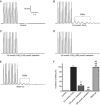
Barbaloin (10-β-D-glucopyranosyl-1,8-dihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-9(10H)-anthracenone) is extracted from the aloe plant and has been reported to have anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antibacterial, and other biological activities. Here, we investigated the effects of barbaloin on cardiac electrophysiology, which has not been reported thus far. Cardiac action potentials (APs) and ionic currents were recorded in isolated rabbit ventricular myocytes using whole-cell patch-clamp technique. Additionally, the antiarrhythmic effect of barbaloin was examined in Langendorff-perfused rabbit hearts. In current-clamp recording, application of barbaloin (100 and 200 μmol/L) dose-dependently reduced the action potential duration (APD) and the maximum depolarization velocity (Vmax), and attenuated APD reverse-rate dependence (RRD) in ventricular myocytes. Furthermore, barbaloin (100 and 200 μmol/L) effectively eliminated ATX II-induced early afterdepolarizations (EADs) and Ca2+-induced delayed afterdepolarizations (DADs) in ventricular myocytes. In voltage-clamp recording, barbaloin (10-200 μmol/L) dose-dependently inhibited L-type calcium current (ICa.L) and peak sodium current (INa.P) with IC50 values of 137.06 and 559.80 μmol/L, respectively. Application of barbaloin (100, 200 μmol/L) decreased ATX II-enhanced late sodium current (INa.L) by 36.6%±3.3% and 71.8%±6.5%, respectively. However, barbaloin up to 800 μmol/L did not affect the inward rectifier potassium current (IK1) or the rapidly activated delayed rectifier potassium current (IKr) in ventricular myocytes. In Langendorff-perfused rabbit hearts, barbaloin (200 μmol/L) significantly inhibited aconitine-induced ventricular arrhythmias. These results demonstrate that barbaloin has potential as an antiarrhythmic drug.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Antiarrhythmic effect of crotonoside by regulating sodium and calcium channels in rabbit ventricular myocytes.Life Sci. 2020 Mar 1;244:117333. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117333. Epub 2020 Jan 18. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31962132
-
Naringin exerts antiarrhythmic effects by inhibiting channel currents in mouse cardiomyocytes.J Electrocardiol. 2023 Sep-Oct;80:69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2023.05.003. Epub 2023 May 13. J Electrocardiol. 2023. PMID: 37262953
-
Isoliensinine Eliminates Afterdepolarizations Through Inhibiting Late Sodium Current and L-Type Calcium Current.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021 Jan;21(1):67-78. doi: 10.1007/s12012-020-09597-z. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 32770463
-
Effects of antiarrhythmic agents and Mg2+ on aconitine-induced arrhythmias.Jpn Heart J. 1996 Sep;37(5):709-18. doi: 10.1536/ihj.37.709. Jpn Heart J. 1996. PMID: 8973383 Review.
-
Cardiac voltage-gated ion channels in safety pharmacology: Review of the landscape leading to the CiPA initiative.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2017 Sep;87:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 Apr 11. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2017. PMID: 28408211 Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin, a Multi-Ion Channel Blocker That Preferentially Blocks Late Na+ Current and Prevents I/R-Induced Arrhythmias.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 21;11:978. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00978. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32973546 Free PMC article.
-
Aloe vera-An Extensive Review Focused on Recent Studies.Foods. 2024 Jul 8;13(13):2155. doi: 10.3390/foods13132155. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38998660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of natural drug modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the treatment of myocardial injury.J Pharm Anal. 2024 Nov;14(11):101034. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101034. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Pharm Anal. 2024. PMID: 39720623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism-based targeting of cardiac arrhythmias by phytochemicals and medicinal herbs: A comprehensive review of preclinical and clinical evidence.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 29;9:990063. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.990063. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36247473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Model Systems for Addressing Mechanism of Arrhythmogenesis in Cardiac Repair.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021 May 29;23(6):72. doi: 10.1007/s11886-021-01498-z. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34050853 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Song XF, Chen XD. Advances in the research of promotion effect of Aloe vera on wound healing and its clinical use. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi 2016; 32: 634–37. - PubMed
-
- Eshun K, He Q. Aloe vera: a valuable ingredient for the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries-a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2004; 44: 91–6. - PubMed
-
- Silva MA, Trevisan G, Hoffmeister C, Rossato MF, Boligon AA, Walker CI, et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of Aloe saponaria Haw in a model of UVB-induced paw sunburn in rats. J Photochem Photobiol B 2014; 133: 47–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

