Serotonin neuron development: shaping molecular and structural identities
- PMID: 29072810
- PMCID: PMC5746461
- DOI: 10.1002/wdev.301
Serotonin neuron development: shaping molecular and structural identities
Abstract
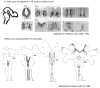
The continuing fascination with serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) as a nervous system chemical messenger began with its discovery in the brains of mammals in 1953. Among the many reasons for this decades-long interest is that the small numbers of neurons that make 5-HT influence the excitability of neural circuits in nearly every region of the brain and spinal cord. A further reason is that 5-HT dysfunction has been linked to a range of psychiatric and neurological disorders many of which have a neurodevelopmental component. This has led to intense interest in understanding 5-HT neuron development with the aim of determining whether early alterations in their generation lead to brain disease susceptibility. Here, we present an overview of the neuroanatomical organization of vertebrate 5-HT neurons, their neurogenesis, and prodigious axonal architectures, which enables the expansive reach of 5-HT neuromodulation in the central nervous system. We review recent findings that have revealed the molecular basis for the tremendous diversity of 5-HT neuron subtypes, the impact of environmental factors on 5-HT neuron development, and how 5-HT axons are topographically organized through disparate signaling pathways. We summarize studies of the gene regulatory networks that control the differentiation, maturation, and maintenance of 5-HT neurons. These studies show that the regulatory factors controlling acquisition of 5-HT-type transmitter identity continue to play critical roles in the functional maturation and the maintenance of 5-HT neurons. New insights are presented into how continuously expressed 5-HT regulatory factors control 5-HT neurons at different stages of life and how the regulatory networks themselves are maintained. WIREs Dev Biol 2018, 7:e301. doi: 10.1002/wdev.301 This article is categorized under: Nervous System Development > Vertebrates: General Principles Gene Expression and Transcriptional Hierarchies > Gene Networks and Genomics Gene Expression and Transcriptional Hierarchies > Cellular Differentiation Nervous System Development > Secondary: Vertebrates: Regional Development.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Twarog BM, Page IH. Serotonin content of some mammalian tissues and urine and a method for its determination. Am J Physiol. 1953 Oct;175(1):157–61. - PubMed
-
- Dahlstrom A, Fuxe K. Evidence for the existence of monamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. I. Demonstration of monamines in the cell bodies of brainstem neurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964;62(Suppl 232):1–55. - PubMed
-
- Flames N, Hobert O. Transcriptional control of the terminal fate of monoaminergic neurons. Annual review of neuroscience. 2011;34:153–84. Epub 2011/06/23. eng. - PubMed
-
- Barnes NM, Sharp T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:1083–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

