Asthma is associated with atherosclerotic artery changes
- PMID: 29073174
- PMCID: PMC5658104
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186820
Asthma is associated with atherosclerotic artery changes
Abstract
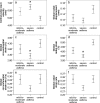
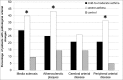
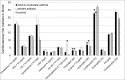
Asthma is a chronic airway inflammation with a potential systemic impact. Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory artery disease. The aim of our study was to prove if there is a correlation between the occurrence of asthma and increased atherosclerotic vessel disorders. Vessel status was compared between mild-to-moderate, severe allergic asthma and matched controls. Measurements of artery stiffness were calculated by central pulse wave velocity, ultrasonographic strain imaging and ankle-brachial index. Atherosclerotic plaque burden was assessed by colour-coded duplex sonography. Additionally, analysis of cardiovascular and asthma blood markers was conducted. Arterial stiffness expressed as an increased central pulse wave velocity and decreased circumferential and radial strains as well as the prevalence of media sclerosis were significantly higher among asthma patients compared to controls. Atherosclerotic plaque burden was relevantly increased in asthma groups vs. controls (severe asthma: 43.1%, mild-to-moderate asthma: 25.0%, control: 14.3% of study participants). Except for the elevated IgE and fibrinogen concentrations as well as leukocyte number there were no relevant differences in the blood parameters between the groups. Allergic asthma is associated with distinct atherosclerotic artery changes compared to the respectively matched control collective. The severity of asthma correlates with more pronounced pathological vessel alternations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Tattersall MC, Guo M, Korcarz CE, Gepner AD, Kaufman JD, Liu KJ, et al. Asthma predicts cardiovascular disease events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015; 35: 1520–1525. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305452 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun WX, Jin D, Li Y, Wang RT. Increased arterial stiffness in stable and severe asthma. Respir Med. 2014; 108: 57–62. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2013.10.021 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cakmak A, Zeyrek D, Cece H, Erel O. The relationship between carotid intima media thickness and oxidative stress in asthmatic children. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2010; 28: 256–261. - PubMed
-
- Ülger Z, Gülen F, Özyürek AR. Abdominal aortic stiffness as a marker of atherosclerosis in childhood-onset asthma: a case-control study. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2015; 26: 8–12. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2014-046 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao RY, St Amand T, Gräbner R, Habenicht AJ, Funk CD. Genetic and pharmacological inhibition of the 5-lipoxygenase/leukotriene pathway in atherosclerotic lesion development in ApoE deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 2009; 203: 395–400. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.07.045 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

