Pegivirus avoids immune recognition but does not attenuate acute-phase disease in a macaque model of HIV infection
- PMID: 29073258
- PMCID: PMC5675458
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006692
Pegivirus avoids immune recognition but does not attenuate acute-phase disease in a macaque model of HIV infection
Abstract
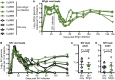
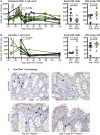
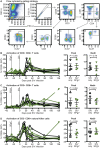
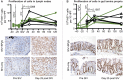
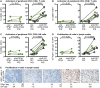
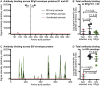
Human pegivirus (HPgV) protects HIV+ people from HIV-associated disease, but the mechanism of this protective effect remains poorly understood. We sequentially infected cynomolgus macaques with simian pegivirus (SPgV) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) to model HIV+HPgV co-infection. SPgV had no effect on acute-phase SIV pathogenesis-as measured by SIV viral load, CD4+ T cell destruction, immune activation, or adaptive immune responses-suggesting that HPgV's protective effect is exerted primarily during the chronic phase of HIV infection. We also examined the immune response to SPgV in unprecedented detail, and found that this virus elicits virtually no activation of the immune system despite persistently high titers in the blood over long periods of time. Overall, this study expands our understanding of the pegiviruses-an understudied group of viruses with a high prevalence in the global human population-and suggests that the protective effect observed in HIV+HPgV co-infected people occurs primarily during the chronic phase of HIV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
JCT is employed by Roche Sequencing Solutions. JCT and the other authors have no other competing interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Stapleton JT, Foung S, Muerhoff AS, Bukh J, Simmonds P (2011) The GB viruses: a review and proposed classification of GBV-A, GBV-C (HGV), and GBV-D in genus Pegivirus within the family Flaviviridae. The Journal of general virology 92: 233–246. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.027490-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhattarai N, Stapleton JT (2012) GB virus C: the good boy virus? Trends in microbiology 20: 124–130. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2012.01.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alter HJ (1997) G-pers creepers, where'd you get those papers? A reassessment of the literature on the hepatitis G virus. Transfusion 37: 569–572. - PubMed
-
- Stapleton JT (2003) GB virus type C/Hepatitis G virus. Seminars in liver disease 23: 137–148. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-39943 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lefrère JJ, Roudot-Thoraval F, Morand-Joubert L, Petit JC, Lerable J, Thauvin M et al. (1999) Carriage of GB virus C/hepatitis G virus RNA is associated with a slower immunologic, virologic, and clinical progression of human immunodeficiency virus disease in coinfected persons. The Journal of infectious diseases 179: 783–789. doi: 10.1086/314671 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

