Denaturing CLIP, dCLIP, Pipeline Identifies Discrete RNA Footprints on Chromatin-Associated Proteins and Reveals that CBX7 Targets 3' UTRs to Regulate mRNA Expression
- PMID: 29073373
- PMCID: PMC5701755
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cels.2017.09.014
Denaturing CLIP, dCLIP, Pipeline Identifies Discrete RNA Footprints on Chromatin-Associated Proteins and Reveals that CBX7 Targets 3' UTRs to Regulate mRNA Expression
Abstract
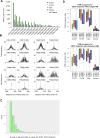
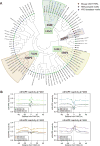
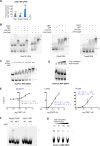
Interaction networks between chromatin complexes and long noncoding RNAs have become a recurrent theme in epigenetic regulation. However, technical limitations have precluded identification of RNA binding motifs for chromatin-associated proteins. Here, we add a denaturation step to UV-crosslink RNA immunoprecipitation (dCLIP) and apply dCLIP to mouse and human chromobox homolog 7 (CBX7), an RNA binding subunit of Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1). In both species, CBX7 predominantly binds 3' UTRs of messenger RNAs. CBX7 binds with a median RNA "footprint" of 171-183 nucleotides, the small size of which facilitates motif identification by bioinformatics. We find four families of consensus RNA motifs in mouse, and independent analysis of human CBX7 dCLIP data identifies similar motifs. Their mutation abolishes CBX7 binding in vitro. Pharmacological intervention with antisense oligonucleotides paradoxically increases CBX7 binding and enhances gene expression. These data support the utility of dCLIP and reveal an unexpected functional interaction between CBX7 and the 3' UTRs of mRNA.
Keywords: 3′ UTR; CBX7; CLIP; ChIP; PRC1; RNA; RNA interactome; bioinformatics; chromatin; epigenetics; polycomb.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Isolation versus Enrichment: dCLIP Enables Stringent Profiling of RNA-Binding Sites.Cell Syst. 2017 Oct 25;5(4):312-314. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2017.10.007. Cell Syst. 2017. PMID: 29073369
References
-
- Bag J, Bhattacharjee RB. Multiple levels of post-transcriptional control of expression of the poly (A)-binding protein. RNA Biol. 2010;7:5–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

