Low prevalence of HPV-driven head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in North-East Italy
- PMID: 29074172
- PMCID: PMC5886905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pvr.2016.07.002
Low prevalence of HPV-driven head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in North-East Italy
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the frequency of Human papillomavirus (HPV)-driven head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) among patients living in North-East Italy, by assessing HPV-DNA positivity in all tumors and additional markers whenever possible.
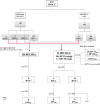
Material and methods: HPV types, viral load, viral RNA, HPV16/18 E6 protein and p16INK4a and pRb expression were determined in primary tumor tissues from 247 HNSCC patients. Tumor-specific HPV seropositivity was analyzed in 102 patients.
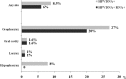
Results: Tumor HPV-DNA prevalence was 8.5% overall (21/247) and 27% in oropharynx (17/63). HPV16 accounted for 95% of all HPV types found. Among HPV-DNA+ tumors, type-concordant HPV E6*I RNA prevalence was 79%. HPV DNA+ RNA+ tumors showed high viral load, up-regulated p16INK4a, down-regulated pRb and presence of HPV16 E6 protein. Eight cases showed tumor-specific HPV seropositivity, all type-concordant with the tumor. Tumors were defined as HPV-driven when positive for HPV-DNA plus 2 additional HPV transformation-related markers.
Conclusion: Relative prevalence of HPV-driven tumors (14 HPV16, 1 HPV58) was 6% overall and 20% among oropharyngeal cancers. In the oropharynx the HPV-driven group showed a trend for better survival versus the HPV-negative group. The relative prevalence of HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer is low in North-East Italy as compared to Western and Northern Europe.
Keywords: HPV antibodies; HPV-driven; HPV-related markers; Head and neck cancer; Oropharyngeal cancer; Prevalence.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- J. Ferlay, E. Steliarova-Foucher and J. Lortet-Tieulent et al., Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012, Eur. J. Cancer 49, 2013, 1374–1403 - PubMed
-
- Ndiaye C., Mena M., Alemany L. HPV DNA, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4a detection in head and neck cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(12):1319–1331. - PubMed
-
- IARC. Human papillomaviruses. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 2011; 100B: 1–475. A review of human carcinogens—Part B: biological agents, vol. 100B, 2011. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 100B (2011) 1–475.
-
- Sturgis E.M., Ang K.K. The epidemic of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer is here: Is it time to change our treatment paradigms? J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2011;9(6):665–673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

